97 IMPROVED CRYOPRESERVATION OF DOMESTIC CAT SPERMATOZOA IN A SOY LECITHIN-BASED EXTENDER
M. M. Vick A , H. L. Bateman A and W. F. Swanson ACincinnati Zoo & Botanical Garden, Center for Conservation and Research of Endangered Wildlife, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 23(1) 153-154 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv23n1Ab97
Published: 7 December 2010
Abstract
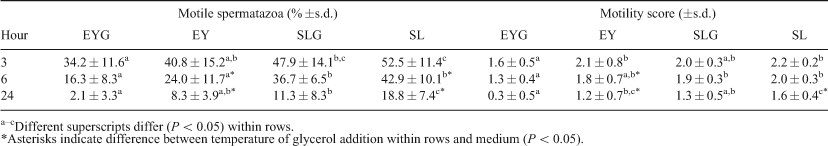
Development of a chemically defined, plant-based cryopreservation media would reduce extender variability and the potential for transmission of zoonotic pathogens compared with traditional egg-yolk-based extenders. The objective of this study was to compare effects of egg yolk- and soy lecithin-based cryopreservation media and the temperature of glycerol addition on sperm parameters following freezing and thawing of domestic cat spermatozoa. Fresh semen was collected by manual stimulation on 3 separate occasions from 4 adult male cats. Each ejaculate was washed to remove seminal plasma, divided into 4 equal aliquots, and extended at room temperature in one of the following treatments: 1) TEST-egg yolk (Irvine Scientific Inc., Santa Ana, CA, USA) medium with 4% glycerol (EYG); 2) TEST-egg yolk, with 4% glycerol added after cooling to 5°C (EY); 3) TES-Tris buffer with soy-lecithin (1%) and 4% glycerol (SLG); and 4) TES-Tris buffer with 1% soy-lecithin, and 4% glycerol added after cooling to 5°C (SL). Sperm progressive motility (%) and rate of progressive movement (scale of 0–5) were evaluated at 0, 1, 3, 6, and 24 h post-thaw. Sperm capacitation (chlortetracycline staining), acrosome integrity (FITC-PNA staining), and DNA integrity (acridine orange staining) were assessed at 15 min post-thaw. Data were exponentially transformed to achieve normal distribution and then subjected to GLM analysis to determine effects of media and temperature of glycerol addition on sperm traits. At 0 and 1 h post-thaw, acrosome integrity, DNA integrity and % sperm motility did not differ (P > 0.05) among treatments. However, % sperm motility was greater in the soy-based media compared to egg yolk-based media at 3, 6, and 24 h post-thaw (Table 1; P < 0.05). A higher percentage of uncapacitated spermatozoa were present in soy-based compared to egg-yolk based cryopreservation media (63.9 ± 9.3 v. 51.2 ± 11.5, respectively; P < 0.05), regardless of temperature of glycerol addition. Finally, addition of glycerol at 5°C resulted in higher % sperm motility compared to room temperature at 6 and 24 h post-thaw in both medium types (Table 1; P < 0.05). Our results suggest that use of a chemically defined, soy-based medium improves long-term motility and capacitation status of frozen–thawed domestic cat spermatozoa compared with cryopreservation in a traditional egg yolk-based extender.
|


