193 PROGESTERONE CONCENTRATIONS AND MESSENGER RNA EXPRESSION OF PROGESTERONE RECEPTORS IN ENDOMETRIAL TISSUE OF BOVINE UTERINE HORN IPSILATERAL AND CONTRALATERAL TO CORPUS LUTEUM
H. Takahashi A , S. Haneda B and M. Matsui BA The United Graduate of Veterinary Sciences Gifu University, Gifu-City, Gifu, Japan;
B Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine, Obihiro-City, Hokkaido, Japan
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 27(1) 187-188 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv27n1Ab193
Published: 4 December 2014
Abstract
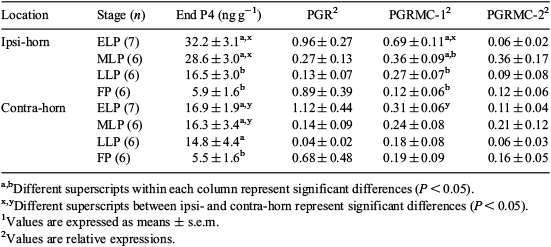
Generally, conception is established in the uterine horn ipsilateral to the corpus luteum (CL) in cattle. When a bovine embryo is transferred into the uterine horn contralateral to CL, conception rate is low. Since progesterone (P4) is essential for the establishment of pregnancy in cattle, locational effects of P4 released from CL at the uterus may cause the differences in fertility. The aim of this study was to determine the endometrial tissue P4 concentrations (EndP4) and the mRNA expression of nuclear progesterone receptor (PGR), and progesterone receptor component-1 (PGRMC-1) and -2 (PGRMC-2) in the endometrial tissues from the ipsi- and contralateral horn. The uteruses of Holstein cows were obtained at a local abattoir. Endometrial tissues were collected from both horns. Based on ovarian morphology, the oestrus cycle of the cow was estimated as follows: early luteal phase (ELP, Day 5–6, Day 0 = oestrus), mid luteal phase (MLP, Day 8–12), late luteal phase (LLP, Day 15–17), and follicular phase (FP, Day 18–20). EndP4 was measured by enzyme immunoassay. Expressions of mRNA were analysed by real-time RT–PCR. Two-way factorial ANOVA and the Steel-Dwass test were applied for a multiple comparison of means. The interrelations between both parameters were expressed by Spearman correlation coefficient. At ELP and MLP, EndP4 in ipsi-horn were higher than that in contra-horn (P < 0.05, see Table 1). Higher mRNA expression of PGRMC-1 in ipsi-horn was observed at ELP compared with contra-horn (P < 0.05). Expressions of mRNA for PGR and PGRMC-2 were similar in both horns. In ipsi-horn at ELP, EndP4 was positively correlated with PGRMC-1 mRNA (r = 0.87, P < 0.05), but was negatively correlated with PGR mRNA (r = –0.76, P < 0.05). However, in contra-horn, EndP4 has no correlation to mRNA expression of P4 receptors. In conclusion, EndP4 was influenced by the location of CL and stage of oestrus cycle. Higher expression of PGRMC-1 mRNA in endometrial tissue of ipsi-horn at ELP might be up-regulated by higher EndP4. These locational effects of CL on uterus may provide an intrauterine environment suitable for embryo development.
|


