28 SIMPLIFIED ACTIVATION METHOD TO IMPROVE THE IN VITRO DEVELOPMENT OF HANDMADE CLONED (HMC) PORCINE EMBRYOS
Y. Du A , Z. Yang A , B. Lv A , L. Lin B , P. M. Kragh B , X. Zhang A , G. Vajta C , H. Yang A and L. Bolund A BA Beijing Genomics Institute, Shenzhen, China;
B Faculty of Agricultural Sciences, University of Aarhus, Aarhus, Denmark;
C PIVET Medical Centre, Perth, Australia
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 21(1) 114-115 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv21n1Ab28
Published: 9 December 2008
Abstract
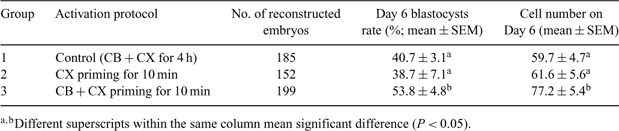
Delayed activation is commonly used in pig somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) where electrical activation is followed by chemical activation. However, chemical incubation of several hours (up to 4 or 6) is logistically not very convenient even though handmade cloning (HMC) could improve the overall efficiency of pig cloning (Du et al. 2007 Theriogenology 68, 1104–1110). It was reported that a brief exposure of cycloheximide (CX) before electrical activation could significantly increase developmental rate and total blastocyst cell number when simultaneous activation was performed in micromanipulator-based pig cloning (Naruse et al. 2007 Theriogenology 68, 709–716). The purpose of our present work is to investigate whether such activation method is also applicable for pig HMC. Data were analyzed by t-test using SPSS (11.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). After 42 h in vitro maturation, cumulus cells were removed. In vitro-cultured porcine fetal fibroblasts were used as donor cells. Cytoplast-fibroblast pairing, electrical fusion and activation of fused cytoplast-fibroblast pairs were performed as described previously (Kragh et al. 2005 Theriogenology 64, 1536–1545; Du et al. 2005 Cloning Stem Cells 7, 199–205). Three groups were compared due to different activation protocol. In Group 1 (control), reconstructed embryos were cultured in porcine zygote medium 3 (PZM3) supplemented with 4 mg mL–1 BSA, 5 μg mL–1 cytochalasin B (CB), and 10 μg mL–1 CX for 4 h. In Group 2 (CX priming), fused pairs and the other halves of cytoplasts were incubated in HEPES-buffered TCM-199 medium supplemented with 10% calf serum, 10 μg mL–1 CX for 10 min just before the second fusion or electrical activation. In Group 3 (CB + CX priming), treatment similar to Group 2 was performed except that additional 5 μg mL–1 CB was added for the 10-min incubation. Reconstructed embryos were in vitro cultured in the well of the well (WOW) system for 6 days. Blastocyst rates and total cell numbers of Day 6 blastocysts were evaluated. As illustrated in Table 1, embryos pretreated with both CB and CX gave the best results, with better blastocyst formation (53.8 ± 4.8%; mean ± SEM) and higher cell number (77.2 ± 5.4) compared to the other 2 groups. Our data suggested that CX and CB priming could be used as a solution to the long chemical incubation in porcine SCNT by HMC, making the embryos more receptive to electrical activation.
|


