290 OPTIMAL OF DOSE OF OVINE PITUITARY GLAND EXTRACT OVAGEN® FOR SUPERSTIMULATION OF BEEF COW DONORS IN ARGENTINA
G. Brogliatti A , J. Villarreal A , L. Cutaia B C , A. Albrech A , A. Garcia Guerra A and G. A. Bó CA Centro Genetico Bovino Eolia S.A., Buenos Aires, Argentina;
B Syntex S.A., Buenos Aires Argentina;
C Instituo de Reproduccion Animal de Cordoba, Cordoba, Argentina
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 21(1) 242-242 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv21n1Ab290
Published: 9 December 2008
Abstract
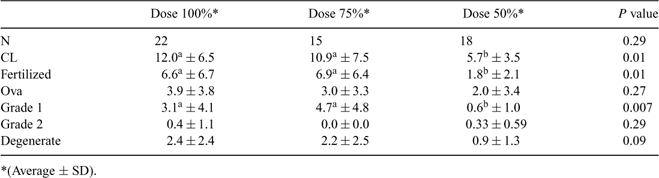
The success of an embryo transfer program is measured by the number of calves born alive by female donor in a given period. The success is influenced by several factors related to the number of ovulations, fertilization rate, and embryo viability (Armstrong D 1993 Theriogenology 39, 7–24). One of the main inconveniences of embryo transfer programs is the variability of superovulatory response to treatments. An experiment was designed to determine the optimal dose of ovine pituitary gland extract Ovagen® (ICPbio, Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand) for inducing superovulation in Aberdeen Angus donor cows. Sixty cycling multiparous donors with a condition score between 3.5 and 4.5 (Scale 1 to 5) were used. All donors received an intravaginal progesterone device DIB (1 g of Progesterone, Syntex, Buenos Aires, Argentina), along with 2 mg of EB (Estradiol Benzoate, Syntex, Buenos Aires, Argentina) and 50 mg of progesterone (Laboratorio Rio de Janeiro, Argentina) on Day 0. Superestimulatory treatment began on Day 4 and donors were randomly assigned to 3 treatment groups according to the total dose of NIADDK-oFSH-Z (Ovagen®) as follows: Group 1, cows received the total dose recommended by the manufacturer (100%* Group), 17.6 mg; Group 2, cows received 75% of the total dose recommended by manufacturer (75% Group), 13.2 mg and Group 3, cows received 50% of the total dose recommended by manufacturer (50% Group), 8.8 mg. All cows received two 150 μg of D+ cloprostenol IM (Ciclase, Syntex) injections on Day 6 given at 12 h interval. DIB was removed on Day 7 a.m. On Day 8 a.m., cows received 0.05 mg of GnRH IM (Gonasyn, Syntex). Fixed time AI was done on Day 8 p.m. and Day 9 a.m. with high quality frozen–thawed semen. On Day 15 embryo collection was performed by non-surgically method and evaluated by developmental stage and quality. The efficiency of superestimulatory response was evaluated by total amount of collected ova-embryos, fertilized ova and embryos Grade 1, 2, and 3, (according to IETS manual). One way AOV test was used to compare variables among groups and results are shown in Table 1. A significant increase in total CL was observed for the groups receiving 75% or 100% of the recommended dose with respect to the group receiving 50% of that dose. There was also a significant greater number of grade 1 embryos for the groups receiving 75% or 100% of the dose than in the group receiving 50% of the recommended dose. There were no differences for any of the evaluated parameters between 75% and 100% dose groups. These results suggest that acceptable superstimulatory responses can be obtained using reduced doses of Ovagen® in Aberdeen Angus donor cows. (*) the percentage makes reference to the total dose recommended by the laboratory of origin.
|
Research supported by Syntex S.A. and Eolia S.A.


