43 COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF PRE-TREATMENT WITH SODIUM CHLORIDE, SUCROSE AND TREHALOSE ON DEVELOPMENTAL COMPETENCE OF PORCINE OOCYTES
L. Lin A C , P. Kragh A C , S. Purup B , Y. Du D , X. Zhang D , H. Yang D , L. Bolund C , H. Callesen A and G. Vajta EA Department of Genetics and Biotechnology, AU, Tjele, Denmark;
B Department of Animal Health, Welfare and Nutrition, AU, Tjele, Denmark;
C Department of Human Genetics, AU, Aarhus, Denmark;
D Beijing Genomics Institute, Shenzhen, China;
E PIVET Medical Centre, Perth, Australia
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 21(1) 121-121 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv21n1Ab43
Published: 9 December 2008
Abstract
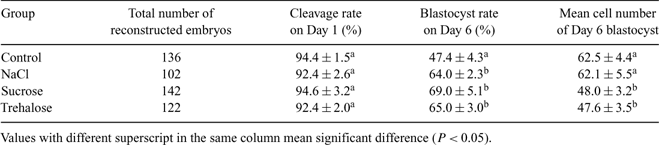
Modified environmental stress was reported to improve the developmental competence and cryotolerance of porcine oocytes, such as high hydrostatic pressure (HHP; Du et al. 2008 Cloning Stem Cells, Epub ahead of print) and osmotic stress (Lin et al. 2008 Reprod. Biomed. Online, in press). HHP also improved the cryotolerance of bovine and murine blastocysts (Pribenszky et al. 2005a Reprod. Dom. Anim. 40, 338–344; Pribenszky et al. 2005b Anim. Reprod. Sci. 87, 143–150). In the present study we compared the effects of NaCl with that of concentrated solutions of two non-permeable osmotic agents, sucrose and trehalose on in vitro maturated oocytes. A total of 2050 slaughterhouse-derived porcine cumulus–oocyte complexes (COCs) were matured for 41–42 h, and then put into 800 μL T2 (HEPES-buffered TCM-199 [Earle’s salts] with 2% cattle serum) supplemented with additional NaCl, sucrose or trehalose with the same osmotic level (588 mOsmol) in 4-well dishes and incubated for 1 h at 38.5°C in air. COCs incubated in T2 under the same conditions without supplementation were used as controls. Subsequently COCs were incubated in IVM medium for 1 h at 38.5°C in 5% CO2 with maximum humidity. After this recovery period cumulus cells were removed with 1 mg mL–1 hyaluronidase and pipetting, and oocytes were used as recipients for somatic nuclear transfer with handmade cloning (HMC) method. Porcine fetal fibroblasts were used as nuclear donor cells. Embryo culture was performed in PZM-3 medium (Yoshioka et al. 2002 Biol. Reprod. 66, 112–119) in 5% CO2, 5% O2 and 90% N2 and maximum humidity. Cleavage and blastocyst rates were checked on Day 1 and Day 6, respectively. Cell numbers were counted after fixation in glycerol containing 20 μg mL–1 Hoechst 33342 fluorochrome on Day 6. t-test was performed for statistical calculations with SPSS 11.0 program (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Results are shown in Table 1. Osmotic stress with both permeable and non-permeable agents increased developmental competence of porcine IVM oocytes. NaCl seems to be more appropriate for the purpose, as the other two components resulted in decreased cell number in blastocysts after somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT). In conclusion, a simple NaCl pre-treatment of oocytes has improved the in vitro efficiency of porcine SCNT.
|
The authors thank Ruth Kristensen, Anette Pedersen, Janne Adamsen and Klaus Villemoes for their help and excellent technical assistance.


