408 HOLSTEIN DONORS RESPONSE USING OR NOT USING ESTRADIOL 17-β IN THE SUPEROVULATORY TREATMENT
S. Fuentes A , D. Ruiz B , P. Vera B , A. Castro B , I. Moreno B , E. Liebana A and J. de la Fuente CA Aberekin SA, Derio, Vizcaya, Spain;
B COVAP SA, Pozoblanco, Cordoba, Spain;
C INIA, Madrid, Spain
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 22(1) 361-361 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv22n1Ab408
Published: 8 December 2009
Abstract
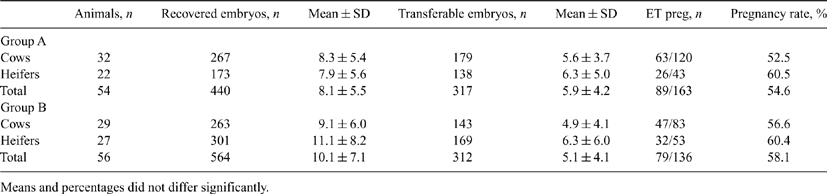
Because of new regulations banning the use of estradiol in the European Union and other countries, the present study was designed to determine the efficacy of an alternative to the use of estradiol 17-β in superovulation of Holstein cows and heifers. A total of 61 lactating cows and 49 heifers (15-18 months old) were divided into 2 groups: Group A (32 cows and 22 heifers) and Group B (29 cows and 27 heifers). Animals in Group A received a CIDR device (Pfizer, Madrid, Spain) for 13 days. At the same time of CIDR insertion and 5 days later, all animals received 2 mL (0.15 mg) of d-cloprostenol (PGF; Veteglan®, Calier, Spain). Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (0.5 mg of gonadorelin; Fertagyl®, Schering-Plough, Carbajosa de la Sagrada, Spain) was administered twice, 36 h after the second PGF and 24 h after CIDR removal. Superovulation treatments were initiated 36 h after the first GnRH, with a total dose of 15 mL (750 IU) of FSH (Pluset®, Calier, Spain) for cows and 11.5 mL (575 IU) for heifers, given in 10 twice-daily injections that decreased in dose. Luteolysis was induced with 0.15 mg of PGF given twice, 12 h before and also at the time of CIDR removal. Animals in Group B received a CIDR device for 7 days. Twenty-four hours after CIDR insertion, all animals received 100 mg of progesterone (Smithkline, Tres Cantos, Spain) and 5 mg of estradiol 17-β (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Beginning on Day 5, animals were superovulated with similar doses of FSH to those used in Group A. Luteolysis was induced with 0.15 mg of PGF given twice, 12 h before CIDR removal and also at the time of removal. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (0.5 mg) was administered at the time of AI. Animals from both groups were inseminated with frozen-thawed semen at 12 and 24 h after the onset of standing estrus. Embryos were recovered nonsurgically 7 days later. A total of 299 frozen-thawed embryos (Freeze Control® CL5500, Bioniche, Belleville, Ontario, Canada) from both groups were transferred in synchronized Holstein heifers. Pregnancy was confirmed by rectal palpation on Day 40 to 45 of gestation. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and results are shown in the table. No significant differences were found between cows and heifers, nor was there a difference between groups. These results showed that the previous superovulatory treatment using progesterone and estradiol can be successfully replaced with the treatment protocol described herein.
|


