Effect of medical students’ values on their clinical decision-making
Mpatisi Moyo 1 4 , Boaz Shulruf 2 , Jennifer Weller 3 , Felicity Goodyear-Smith 11 University of Auckland, Department of General Practice and Primary Health Care, Auckland, New Zealand
2 University of New South Wales, Medical Education, Sydney, Australia
3 University of Auckland, Centre for Medical and Health Science Education, Auckland, New Zealand
4 Corresponding author. Email: mphatomnz@gmail.com
Journal of Primary Health Care 11(1) 64-74 https://doi.org/10.1071/HC18055
Published: 15 February 2019
Journal Compilation © Royal New Zealand College of General Practitioners 2019.
This is an open access article licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Personal and professional values of health-care practitioners influence their clinical decisions.
AIM: To investigate how medical students’ values influence their clinical decisions.
METHODS: Values of 117 medical students were measured using an instrument we developed, the Healthcare Practitioner Values Scale. Factors that students consider in clinical decision-making were identified in four clinical scenarios using qualitative coding. Differences in values between students who considered given factors in decision-making and students who did not consider the same factors were analysed. Random effects models were used to investigate which differences were explained by variation in the clinical scenarios and factors considered in decision-making.
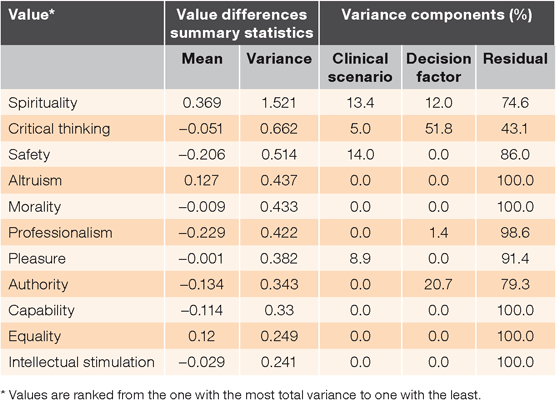
RESULTS: Six factors that students consider in clinical decision-making were identified and grouped into three categories: patient-centred (patient perspective, family and social circumstances); clinical (patient safety, symptoms and treatment efficacy); and situational factors (health-care practitioner self-awareness and service cost). Students who prioritised spirituality placed more emphasis on patient-centred factors, and less emphasis on clinical factors in different scenarios; students who prioritised critical thinking placed less emphasis on patient-centred factors; and students who prioritised capability, professionalism and safety values placed more emphasis on situational factors. Total proportion of variance in value differences explained by factors and clinical scenarios was 25.2% for spirituality and 56.2% for critical thinking.
DISCUSSION: Students who prioritise different values consider different factors in their clinical decisions. Spirituality and critical thinking values are more likely to influence students’ decision-making approaches than other values. Improving students’ awareness of how their own values influence their decisions can help them improve their clinical decision-making.
KEYWORDS: Decision-making; social values; students; medical; New Zealand; professional practice
| WHAT GAP THIS FILLS |
| What is already known: Personal and professional values of health-care practitioners influence their clinical decisions. While the effects of values on decisions involving general ethical dilemmas have been researched, there is a gap in our knowledge about how values influence decision-making in everyday clinical practice in cases where there is no clear consensus on which decisions are right or wrong, or best for patients. |
| What this study adds: Students who prioritise different values consider different factors in their clinical decisions. Spirituality and critical thinking values are more likely to influence students’ decision-making approaches than other values. Improving students’ awareness of how their own values influence their decisions may help them improve their clinical decision-making and address any unconscious biases. |
Introduction
Decision-making is influenced by a variety of factors such as individuals’ experiences, skills, values, habits, personal perceptions and availability of information and time.1,2 Clinical decision-making may also be influenced by personal and professional values of health-care practitioners,3,4 resulting in personal biases in clinical decisions, which can compromise the quality of patient care. Clinicians may be unaware of their biases.5 To reduce health-care practitioner biases and facilitate patient involvement in decision-making, current practices promote patient-centred and shared decision-making models that incorporate the values, preferences and social circumstances of patients into clinical decisions.6–8 Some educators have suggested that improving the health-care practitioners’ awareness of their own values and how these values influence their decision-making may help reduce their personal biases and deliver more patient-centred decisions.9,10
There is little research on the relationship between clinicians’ values and decision-making,11,12 and whatever is available has largely focused on decision-making on general ethical dilemmas, not on situations typical in clinical practice. Existing studies focus on the relationship between values and specific skills including problem-solving in nursing students,13 ethical decision-making in medical and dental students,11 and moral development in medical students.12 The nursing student study13 investigated students’ decision-making abilities using an instrument that measured their confidence with problem-solving,14 and the other two11,12 measured decision-making abilities using case-based assessments, with students selecting decision alternatives from a panel that included some alternatives that were ethically correct or preferable to others. In these studies, the case scenarios used were general ethical dilemmas, not specific to decision-making in clinician–patient interactions.
Nevertheless, findings from these studies11–13 and others15–17 indicate associations between values and decision-making. Nursing students who prioritised values of truth and human dignity, as defined by the American Association of Nursing Colleges,18 showed greater confidence in problem-solving than other students.13 Conversely, medical and dental students who prioritised the value of comfort over equality, as measured by the Rokeach Values Survey,19 showed poorer ethical decision-making abilities than other students.11 Medical students who prioritised the value of universalism, as measured by the Schwart Values Survey,20 showed greater moral decision-making abilities than other students, while students who prioritised the values of power and achievement showed poorer moral decision-making abilities.12
In contrast to the general ethical dilemmas in these studies,11,12 decision-making in everyday practice often involves cases where there is no consensus on which decisions are right or wrong, or best for individual patients.21,22 Clinical decisions often involve consideration of many factors including the clinical problem, investigation data, patients’ values, patients’ family and social circumstances, practice environment, organisation and legislation environments, and health-care practitioners’ capabilities and values.23,24 Successfully negotiating these factors to make decisions that have optimum outcomes for patients reflects clinicians’ decision-making skills in the context of actual practice.25
Our aim was to identify how medical students’ values influence their decision-making with patients in everyday general practice situations. Rather than use multiple choice testing with given right and wrong alternatives to measure students’ decision-making,11,12 we aimed to identify the factors different students consider in decision-making in different clinical contexts, and investigate how these are influenced by the students’ values. We used a value measurement instrument designed to measure values relevant to decision-making in health care.26,27 This instrument uses Schwartz’s values model20 as a framework, but its content is contextualised to health-care practice. The advantages of this approach are that the framework comprehensively covers key values that guide human decision-making, and it has been validated across cultures.20,28,29
Our specific objectives were to determine:
-
What factors are commonly considered by medical students in clinical decision-making in different clinical contexts?
-
How do differences in value priorities between medical students influence their decision-making in given clinical contexts?
-
Which values are likely to influence the type of factors that medical students consider in making decisions in different clinical contexts?
Methods
Participants and measures
We invited into the study all students completing Year 5 in the 6-year medical programme at the University of Auckland. Years 4 and 5 focus on hospital and community clinical practice in disciplines including general practice, psychiatry, medicine and surgery. Problem-based and case-based learning are used. Students are exposed to complex real-world contexts to prepare them for their trainee internship in Year 6. The study was approved by the University of Auckland Human Participants Ethics Committee (Reference 011073/2014). The survey was conducted in two parts:
Part one: health-care practitioner values scale
The health-care practitioner values scale (HPVS) organises personal and professional values of health-care practitioners identified from literature26,27 within the Schwartz values model.20 The HPVS incorporates 11 health-care practitioner personal and professional values: authority, capability, pleasure, intellectual stimulation, critical thinking, equality, altruism, spirituality, tradition, professionalism and safety.26 Participants were asked to rank these values according to the importance of each to them as a guiding principle in their health-care practice. The most important value was ranked 1 and the least important ranked 11.
Part two: clinical decision-making
Participants were asked to list as many issues and considerations that matter to them and their patient in coming to a clinical decision for each of four clinical scenarios (Table 1). They were not required to rank them. The scenarios represented cases where there are no clear-cut right or wrong decisions. They were developed and validated with a group of general practitioners. A worked example and the following instruction for completing this section were given: ‘For each of the following four scenarios please list as many things as you think may be relevant (e.g. in bullet point form) about the issues and considerations that would matter to you and your patient in coming to a clinical decision’.
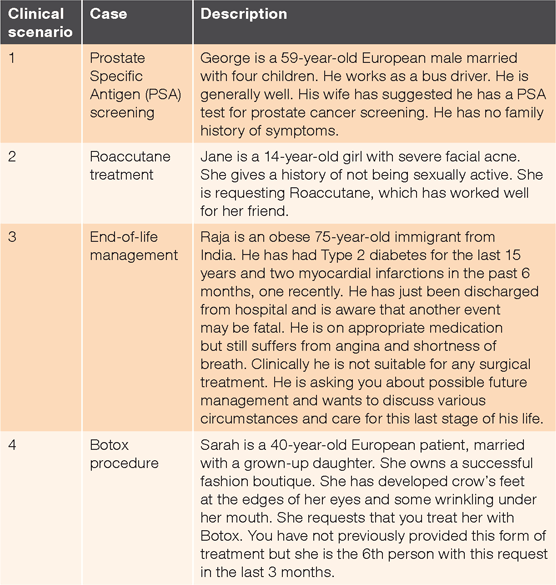
|
Data analyses
Objective 1. Content analysis of clinical decision-making
We used a general inductive approach for thematic analysis of qualitative data30 to identify factors considered in making a decision for each clinical scenario. Key factors were identified, coded and synthesised for each scenario by two researchers independently. Discrepancies were resolved with adjudication.
Objective 2. Analysis of differences in value priorities between students who selected different factors in their clinical decision-making
For each clinical scenario, ranked value priorities (measured by ranking) for participants who identified a particular factor in making their decision were compared between participants who identified or did not identify a factor as important. We used Welch’s t-test to evaluate the difference between mean value priorities, and Cohen’s d to estimate the effect size of the differences. Our null hypothesis was that there were no differences in mean value priorities of participants who did and did not consider a particular factor in making a clinical decision in a given scenario.
To highlight key differences in value priorities across factors in the four clinical scenarios, data with significant differences (P < 0.05) and significant effect sizes (Cohen’s d > 0.3) were tabulated. The patterns in the selected data were analysed to understand how differences in value priorities between medical students influenced their choice of factors in given clinical contexts.
Objective 3. Analysis of variance components of differences in value priorities across factors and clinical scenarios for each value using random effects models
For all clinical scenario and factor combinations, we computed differences in value priorities between students who considered a given factor in their decision and students who did not consider the same factor. For example, 24 data points for the value of altruism consisted of differences in altruism ranks between students who considered the patient’s perspective and those who did not in each of the four clinical scenarios, differences in altruism ranks between students who considered family and social circumstances and those who did not, and so on for each decision factor in the four scenarios. Similar differences were computed for each value in turn.
We explored variation in value priority differences (rank differences) for each value using a boxplot. If given values showed larger variation in rank differences across factors and scenarios, this would indicate that these values were more likely to influence the factors students considered in decision-making in different contexts than other values. We then analysed the rank differences for each value using a random effects model. Our rationale was that there are many clinical scenarios (contexts) that can arise in clinical practice, and many factors that can be considered in a clinical scenario, so we analysed the clinical scenarios and the factors as random observations from populations of clinical scenarios and factors. For each value, we used a random effects model to estimate variance components for the rank differences between students who considered a given factor in their decision and those who did not. The rank differences were modelled as a dependent variable against clinical scenarios and factors considered in decision-making, which were modelled as random independent variables. The variance components estimated were the proportions of variation in rank differences that were explained by random clinical scenarios, random factors in decision-making and residual error for each value. If the proportion of variation explained by clinical scenarios or factors considered in decision-making was significant for particular values, this would imply that the given values were likely to influence the choice of factors considered in decision-making in different clinical contexts.
Results
From a class of 240 medical students, 117 (49%) participated in our survey.
Common factors considered in clinical decision-making
We identified six major factors students considered in decision-making: patient perspective, family and social circumstances, patient safety, symptoms and treatment efficacy, health-care practitioner self-awareness, and service cost (Table 2). We grouped these into three categories by considering the aspects of clinical decision-making on which they focused: patient-centred (patient perspective, family and social circumstances); clinical (patient safety, symptoms and treatment efficacy); and situational (health-care practitioner self-awareness, service cost). Inter-rater agreement in organising text segments into the six decision factors was 96.5%. We reached full consensus on the classification of the texts into themes after adjudication.

|
Comparison of value priorities between students who selected different factors in making clinical decisions
Significant value priority differences (P < 0.05, Cohen’s d > 0.3) between students who selected different factors in making clinical decisions are shown in Table 3 and are summarised below:
(i) In the End-of-life and Botox scenarios, students who ranked spirituality higher considered patient-centred factors more frequently.
(ii) In the prostate specific antigen (PSA), Roaccutane and End-of-life scenarios, students who ranked spirituality higher considered clinical factors less frequently.
(iii) In the Roaccutane and Botox scenarios, students who ranked critical-thinking higher considered patient-centred factors less frequently.
(iv) In the Botox, End-of-life and PSA scenarios, students who considered situational factors ranked capability, professionalism and safety values higher, respectively.

|
Analysis of variance components of differences in value priorities across factors and clinical scenarios for each value using random effects models
In the data from all clinical scenarios, spirituality and critical thinking showed the greatest variations in value priority differences between students who considered a given factor in their decision and students who did not consider the same factor (Fig. 1). Value priority differences for altruism, authority, capability, equality and morality also showed considerably higher variation compared to values of intellectual stimulation, pleasure, professionalism and safety. From variance component analysis, the total proportion of variance in value priority differences explained by random decision factors and clinical scenarios was highest for critical thinking (56%) and spirituality (25%) values (Table 4; Fig. 2).
|
Discussion
Our content analysis identified six major factors that medical students consider in clinical decision-making, and we organised these into three categories: patient-centred, clinical and situational. Overall, our findings suggest that spirituality and critical thinking are the two values that are most likely to influence factors medical students consider in their clinical decisions. Students who prioritise spirituality are more likely to consider patient-centred factors, and less likely to consider clinical factors than other students in some contexts. Students who prioritise critical-thinking are less likely to consider patient-centred factors in some contexts compared to other students. Students who prioritise capability, professionalism and safety values are more likely to consider situational factors relevant to a given case than other students.
The factors influencing clinical decision-making that we identified in this study are consistent with factors discussed in literature.24,31 Our new finding is that patient-centred factors were the most prominent factors medical students considered in their decision-making. Patient-centred decision-making approaches have been widely promoted in medical education in recent decades, and medical students may also adopt patient-centred decision-making approaches as a result.32–34 Other studies also indicate that medical students demonstrate considerable patient-centred attitudes in their clinical practice.35–37
We found that spirituality was the most prominent value associated with differences in students’ decision-making approaches. This is consistent with other studies, which indicate that many clinicians acknowledge that their spirituality influences their clinical decisions.38–41 Specifically, our findings indicate that students who prioritise spirituality favour patient-centred factors in decision-making. This agrees with one study that showed a positive correlation between spirituality and patient-centred approaches to decision-making.42 Furthermore, we found that the influence of spirituality on clinical decision-making depends on the clinical context, which is consistent with other studies.38,43,44 Clinicians are more willing to consider spirituality in contexts involving dying than in any other contexts.43 Finally, our finding on the negative correlation between spirituality and evaluation of clinical factors in clinical decision-making is a concern. We found no studies exploring this relationship, so it may require further investigation.
Critical thinking was the second most prominent value associated with differences in students’ decision-making approaches, after spirituality. In two scenarios where patients requested specific treatments, we observed that students who ranked the critical thinking value high were less inclined to consider the patient’s perspective. This could imply that students who prioritise critical-thinking may place less emphasis on patient-centred aspects of clinical decision-making. The fact that critical thinking is generally associated more with analytic reasoning from evidence-based data45 rather than decision-making guided by interpersonal interactions46 may partly support our finding. Students who value critical thinking may rely on analysis of evidence-based data and overlook incorporating patients’ perspectives into their decisions. However, we found no other studies on the relationship between critical thinking and patient-centeredness to corroborate these findings.
Students who prioritised capability, professionalism and safety values were more inclined to consider situational factors (health-care practitioner self-awareness, service cost). Students who prioritise these values tend to reflect more on their own values, competence and cost of health-care services than other students, which is likely to improve the quality of their decisions. Clinicians who are aware of their own values and limits of competency can reflect on these issues to enable them to consider all relevant information and perspectives in their clinical decisions.10 Furthermore, clinicians have a responsibility to manage health-care resources, and their awareness of clinical costs can improve equitable distribution of health care.47
We observed some significant differences in authority and morality value priorities between students who considered different factors in their decisions, but could not draw consistent patterns for these differences across our data. Some literature suggests that health-care practitioners’ authority and morality values influence their clinical decisions.48 We found no meaningful differences in value rankings for altruism, equality, intellectual stimulation and pleasure. These values do not appear to have a significant influence on the factors students consider in clinical decision-making. Altruism and equality values are strongly promoted as essential values for students and health-care practitioners across health-care professional groups, while intellectual stimulation and pleasure are rarely recognised as relevant values in clinical practice.27 It is possible that because these values are either universally promoted or universally shunned in health-care education, they hardly motivate different decision-making approaches in students. However, it is also possible that the scenarios we investigated did not adequately address these values.
Strengths and limitations
While previous studies relating health-care students’ values to decision-making have used general measures for values and decision-making,11–13 we used a published value instrument specifically designed to measure personal and professional values relevant to decision-making in health care.27 We qualitatively coded text responses to identify factors students considered in clinical decision-making. We achieved a high agreement between two raters on the factors identified, indicating the robustness of our approach. However, the number of scenarios and therefore the range of clinical contexts we investigated was small. This may limit our ability to generalise our findings beyond clinical contexts similar to those used in this study.
Our curriculum emphasises both evidence-based and patient-centred decision-making as they apply to different contexts. Nevertheless, we found evidence that students may be inclined to use clinical evidence more, or patient-centredness more, depending on their value priorities.
We acknowledge the limitations in our study; the limited clinical experience of students and that our findings could vary with experienced health-care practitioners; the limited generalisation of our findings to other schools and cultures because of variations in curricula and value preferences across schools and cultures; and our modest response rate (49%). However, we believe our sample was representative of the class because all students had an opportunity to participate.
Implications
Overall, our findings suggest that medical students who prioritise values differently consider different factors when making decisions about patient care. The students are more or less likely to consider or ignore some factors in decision-making in different contexts depending on their value priorities. This is congruent with decision theories that suggest that the choice of factors considered in any given problem partly depends on the decision-maker’s personal characteristics and values.49–51 Therefore, improving medical students’ and clinicians’ awareness of the influence of specific values on their clinical decisions can help them recognise and potentially moderate their personal biases to consider all relevant factors in a given clinical situation, to make informed high-quality decisions on patient care. This is an area for future research. Finally, educators can exploit the knowledge we present on explicit relations between values and factors in decision-making to enhance teaching strategies on clinical decision-making.
Funding
None.
Competing interests
None.
References
[1] Kahneman D. Representativeness Revisited: Attribute Substitution in Intuitive Judgment. UK: Cambridge University Press; 2002.[2] Evans RG. Patient centred medicine: reason, emotion, and human spirit? Some philosophical reflections on being with patients. Med Humanit. 2003; 29 8–14.
| Patient centred medicine: reason, emotion, and human spirit? Some philosophical reflections on being with patients.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23671167PubMed |
[3] Smith TS, McGuire JM, Abbott DW, et al. Clinical ethical decision making: an investigation of the rationales used to justify doing less than one believes one should. Prof Psychol Res Pr. 1991; 22 235–39.
| Clinical ethical decision making: an investigation of the rationales used to justify doing less than one believes one should.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 11653958PubMed |
[4] Gross DR, Robinson SE. Ethics, violence, and counseling: hear no evil, see no evil, speak no evil? J Couns Dev. 1987; 65 340–4.
| Ethics, violence, and counseling: hear no evil, see no evil, speak no evil?Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[5] Teal CR, Street RL. Critical elements of culturally competent communication in the medical encounter: a review and model. Soc Sci Med. 2009; 68 533–43.
| Critical elements of culturally competent communication in the medical encounter: a review and model.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19019520PubMed |
[6] Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality Health Care in America. Report Brief: Crossing the Quality Chasm. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 2001.
[7] Deber RB. Physicians in health care management: 8. The patient-physician partnership: decision making, problem solving and the desire to participate. CMAJ. 1994; 151 423–27.
| 8055402PubMed |
[8] O'Connor AM, Llewellyn-Thomas HA, Flood AB. Modifying unwarranted variations in health care: shared decision making using patient decision aids. Health Aff. 2004; 23 VAR63–72.
| Modifying unwarranted variations in health care: shared decision making using patient decision aids.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[9] Duggan PS, Geller G, Cooper LA, et al. The moral nature of patient-centeredness: Is it “just the right thing to do”? Patient Educ Couns. 2006; 62 271–6.
| The moral nature of patient-centeredness: Is it “just the right thing to do”?Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16356677PubMed |
[10] Epstein RM. Mindful practice. JAMA. 1999; 282 833–9.
| Mindful practice.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 10478689PubMed |
[11] McCabe DL, Dukerich JM, Dutton JE. Values and ethical decision-making among professional school students: a study of dental and medical students. Prof Ethics. 1992; 1 117–36.
| Values and ethical decision-making among professional school students: a study of dental and medical students.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 11652111PubMed |
[12] Helkama K, Uutela A, Pohjanheimo E, et al. Moral reasoning and values in medical school: a longitudinal study in Finland. Scand J Educ Res. 2003; 47 399–411.
| Moral reasoning and values in medical school: a longitudinal study in Finland.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[13] Altun I. The perceived problem solving ability and values of student nurses and midwives. Nurse Educ Today. 2003; 23 575–84.
| The perceived problem solving ability and values of student nurses and midwives.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 14554111PubMed |
[14] Heppner PP, Petersen CH. The development and implications of a personal problem-solving inventory. J Couns Psychol. 1982; 29 66–75.
| The development and implications of a personal problem-solving inventory.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[15] Feather N. Moral judgement and human values. Br J Soc Psychol. 1988; 27 239–46.
| Moral judgement and human values.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[16] Pohjanheimo E. Moral reasoning and moral values. Acta Psychol Fennica. 1988; 10 66–7.
[17] Helkama K. The development of moral reasoning and moral values. Acta Psychol Fennica. 1983; 9 99–111.
[18] American Association of Colleges of Nursing. Essentials of college and university education for professional nursing: Final report. Washington, DC: American Association of Colleges of Nursing; 1986.
[19] Rokeach M. The Nature of Human Values. New York: Free Press; 1973.
[20] Schwartz SH. Universals in the content and structure of values: theoretical advances and empirical tests in 20 countries. Adv Experiment Soc Psychol. 1992; 25 1–65.
[21] Forman EN, Ladd RE. Telling the truth in the face of medical uncertainty and disagreement. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1989; 11 463–6.
| 2618984PubMed |
[22] Logan RL, Scott PJ. Uncertainty in clinical practice: implications for quality and costs of health care. Lancet. 1996; 347 595–8.
| Uncertainty in clinical practice: implications for quality and costs of health care.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 8596325PubMed |
[23] Gartner J, Harmatz M, Hohmann A, et al. The effect of patient and clinician ideology on clinical judgment: a study of ideological countertransference. Psychotherapy. 1990; 27 98
| The effect of patient and clinician ideology on clinical judgment: a study of ideological countertransference.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[24] Higgs J. Clinical Reasoning in the Health Professions. Sydney: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2008.
[25] Norman G. Research in clinical reasoning: past history and current trends. Med Educ. 2005; 39 418–27.
| Research in clinical reasoning: past history and current trends.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15813765PubMed |
[26] Moyo M. The Impact of Medical Students’ Values on their Clinical Decision-Making. PhD Thesis. Auckland: University of Auckland, New Zealand; 2016.
[27] Moyo M, Goodyear-Smith FA, Weller J, et al. Healthcare practitioners’ personal and professional values. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2016; 21 257–86.
| 26215664PubMed |
[28] Braithwaite VA, Law H. Structure of human values: testing the adequacy of the Rokeach Value Survey. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1985; 49 250
| Structure of human values: testing the adequacy of the Rokeach Value Survey.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[29] Schwartz SH. Are there universal aspects in the structure and contents of human values? J Soc Issues. 1994; 50 19–45.
| Are there universal aspects in the structure and contents of human values?Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[30] Thomas DR. A general inductive approach for analyzing qualitative evaluation data. Am J Eval. 2006; 27 237–46.
| A general inductive approach for analyzing qualitative evaluation data.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[31] Hagbaghery MA, Salsali M, Ahmadi F. The factors facilitating and inhibiting effective clinical decision-making in nursing: a qualitative study. BMC Nurs. 2004; 3 2
| The factors facilitating and inhibiting effective clinical decision-making in nursing: a qualitative study.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 15068484PubMed |
[32] Christianson CE, McBride RB, Vari RC, et al. From traditional to patient-centered learning: curriculum change as an intervention for changing institutional culture and promoting professionalism in undergraduate medical education. Acad Med. 2007; 82 1079–88.
| From traditional to patient-centered learning: curriculum change as an intervention for changing institutional culture and promoting professionalism in undergraduate medical education.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 17971696PubMed |
[33] Markakis KM, Beckman HB, Suchman AL, et al. The path to professionalism: cultivating humanistic values and attitudes in residency training. Acad Med. 2000; 75 141–49.
| The path to professionalism: cultivating humanistic values and attitudes in residency training.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 10693844PubMed |
[34] Laine C, Davidoff F. Patient-centered medicine. A professional evolution. JAMA. 1996; 275 152–6.
| Patient-centered medicine. A professional evolution.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 8531314PubMed |
[35] Haidet P, Dains JE, Paterniti DA, et al. Medical student attitudes toward the doctor–patient relationship. Med Educ. 2002; 36 568–74.
| Medical student attitudes toward the doctor–patient relationship.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 12047673PubMed |
[36] Tsimtsiou Z, Kerasidou O, Efstathiou N, et al. Medical students’ attitudes toward patient-centred care: a longitudinal survey. Med Educ. 2007; 41 146–53.
| Medical students’ attitudes toward patient-centred care: a longitudinal survey.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 17269947PubMed |
[37] Wahlqvist M, Gunnarsson RK, Dahlgren G, et al. Patient-centred attitudes among medical students: gender and work experience in health care make a difference. Med Teach. 2010; 32 e191–98.
| Patient-centred attitudes among medical students: gender and work experience in health care make a difference.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 20353319PubMed |
[38] Ramondetta L, Brown A, Richardson G, et al. Religious and spiritual beliefs of gynecologic oncologists may influence medical decision making. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011; 21 573
| Religious and spiritual beliefs of gynecologic oncologists may influence medical decision making.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 21436706PubMed |
[39] Ecklund EH, Cadge W, Gage EA, et al. The religious and spiritual beliefs and practices of academic pediatric oncologists in the United States. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2007; 29 736–42.
| The religious and spiritual beliefs and practices of academic pediatric oncologists in the United States.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 17984690PubMed |
[40] Curlin FA, Lantos JD, Roach CJ, et al. Religious characteristics of US physicians. J Gen Intern Med. 2005; 20 629–34.
| Religious characteristics of US physicians.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16050858PubMed |
[41] Catlin EA, Cadge W, Ecklund EH, et al. The spiritual and religious identities, beliefs, and practices of academic pediatricians in the United States. Acad Med. 2008; 83 1146–52.
| The spiritual and religious identities, beliefs, and practices of academic pediatricians in the United States.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19202482PubMed |
[42] Pawlikowski J, Sak JJ, Marczewski K. Physicians’ religiosity and attitudes towards patients. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2012; 19 503–7.
| 23020047PubMed |
[43] Monroe MH, Bynum D, Susi B, et al. Primary care physician preferences regarding spiritual behavior in medical practice. Arch Intern Med. 2003; 163 2751–6.
| Primary care physician preferences regarding spiritual behavior in medical practice.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 14662629PubMed |
[44] Voltmer E, Büssing A, Koenig HG, et al. Religiosity/spirituality of German doctors in private practice and likelihood of addressing R/S issues with patients. J Relig Health. 2014; 53 1741–52.
| Religiosity/spirituality of German doctors in private practice and likelihood of addressing R/S issues with patients.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 24077926PubMed |
[45] Facione NC, Facione PA, Sanchez CA. Critical thinking disposition as a measure of competent clinical judgment: the development of the California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory. J Nurs Educ. 1994; 33 345–50.
| 7799093PubMed |
[46] Kahlke R, White J. Critical thinking in health sciences education: considering “Three Waves”. Creat Educ. 2013; 4 21
| Critical thinking in health sciences education: considering “Three Waves”.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[47] Fowkes FG. Doctors’ knowledge of the costs of medical care. Med Educ. 1985; 19 113–7.
| Doctors’ knowledge of the costs of medical care.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 3982310PubMed |
[48] Tilburt JC, James KM, Jenkins SM, et al. “Righteous Minds” in health care: measurement and explanatory value of social intuitionism in accounting for the moral judgments in a sample of US physicians. PLoS One. 2013; 8 e73379.
| “Righteous Minds” in health care: measurement and explanatory value of social intuitionism in accounting for the moral judgments in a sample of US physicians.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 24023864PubMed |
[49] Tversky A, Kahneman D. Rational choice and the framing of decisions. J Bus. 1986; 59 S251–78.
| Rational choice and the framing of decisions.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
[50] Tversky A, Kahneman D. The framing of decisions and the psychology of choice. Science. 1981; 211 453–8.
| The framing of decisions and the psychology of choice.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 7455683PubMed |
[51] De Martino B, Kumaran D, Seymour B, et al. Frames, biases, and rational decision-making in the human brain. Science. 2006; 313 684–7.
| Frames, biases, and rational decision-making in the human brain.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16888142PubMed |




