60 EFFECT OF CYTOPLASMIC VOLUME ON DEVELOPMENTAL COMPETENCE OF HAND-GUIDED CLONED BUFFALO (BUBALUS BUBALIS) EMBRYOS
S. K. Panda A , A. George A , A. P. Saha A , R. Sharma A , N. M. Kamble A , R. S. Manik A , M. S. Chauhan A , P. Palta A and S. K. Singla ANational Dairy Research Institute, Karnal, Haryana, India
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 23(1) 135-136 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv23n1Ab60
Published: 7 December 2010
Abstract
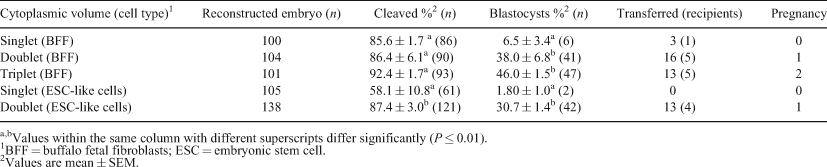
Despite recent successes in the birth of buffalo calves cloned through SCNT or hand-guided cloning (HGC), the cloning efficiency is very low in this species because of lack of information on factors that influence it. The goal of this study was to examine the effects of cytoplasmic volume on the developmental competence of cloned buffalo embryos produced by HGC. In vitro matured oocytes were stripped of their cumulus investment and zona pellucida using hyaluronidase and pronase, respectively. Protrusion cone-guided bisection of zona-free oocytes was performed to remove the nucleus. For reconstructing control HGC embryos, 2 enucleated oocytes (demi-cytoplasts) were fused with a single somatic cell. For reconstruction of embryos with lower or higher cytoplasmic volume, 1 or 3 demi-cytoplasts were fused, respectively, with the donor somatic cell. 2 different cell types, i.e. buffalo fetal fibroblasts (BFF) between passage 10 and 15 and buffalo embryonic stem cell (ESC)-like cells between passage 22 and 25 were used as nuclear donors in 2 different experiments. Data were analysed by 1-way ANOVA after arcsine transformation of percentage values. For BFF, the blastocyst rate for doublet and triplet embryos were significantly higher (P ≤ 0.01) than that for singlet embryos despite the cleavage rate for the 3 groups being similar. For the ESC-like cells, the cleavage and the blastocyst rate were significantly lower (P ≤ 0.01) for the singlet than that for the doublet embryos. The pregnancies were established only in doublet and triplet embryo groups using BFF cells and in the doublet embryo group using ESC-like cells. These results indicate that increasing the cytoplasmic volume could be helpful in improving cloning efficiency in terms of blastocyst production rate in buffaloes.
|
This work was funded by NAIP grant C 2-1-(5)/2007 to SKS.


