228 Effect of seminal plasma on the interval to application of equine chorionic gonadotrophin for the recovery of cumulus-oocyte complexes in alpacas (Vicugna pacos)
W. F. Huanca A , J. M. Palomino C , J. C. Villanueva A , J. Malaga B and W. Huanca AA Laboratory of Animal Reproduction, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Lima, Lima, Perú;
B Faculty of Veterinary Medicine and Zootechny, Universidad Nacional del Altiplano, Puno, Puno, Perú;
C Boviteq, Saint Hyacinthe, QC, Canada
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 32(2) 242-242 https://doi.org/10.1071/RDv32n2Ab228
Published: 2 December 2019
Abstract
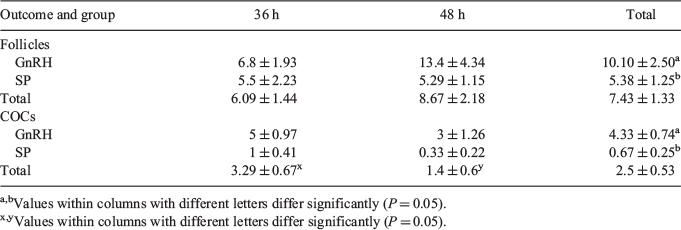
Alpacas as other camelids are induced ovulators and require an external stimulus-mounting by the male-for ovulation. NGF-β, protein present in the seminal plasma (SP) is reported as being responsible for stimulating ovulation. However, limited information exists on the effect of ovulation inducers in the new follicular wave emergence with application on protocols of superstimulation. The aim of the study was to determine the effect of two ovulation induced techniques and two different times on the interval to application of equine chorionic gonadotrophin (eCG) for the ovarian superstimulation for the recovery of COCs by ovum pick- up (OPU). Alpacas were evaluated by transrectal ultrasonography with an Aloka SSD 500 ultrasound and transducer (7.5 MHz) to determine the presence of a dominant follicle = 7 mm. A 2 × 2 experimental design was used with adult female alpacas, 6 to 8 years old, which were assigned to one of the treatments when a dominant follicle = 7 mm was present. Alpacas were assigned randomly 1 of 2 groups (Day 0) in which follicular ovulation was induced by seminal plasma 1 mL IM (SP, n = 13; group 1) with application of 650 IU of eCG at 36 h (n = 6) or 48 h (n = 7) post-application of SP, or by GnRH with 0.008 mg of Buserelin IM (GnRH, n = 10; group 2) with application of 650 IU eCG at 36 h (n = 5) or 48 h (n = 5) post-application of GnRH. On Day 7, COCs were counted and the OPU procedure was performed in every group. Data were analysed using ANOVA. Results are presented in Table 1. In conclusion, both inducers of ovulation and both times of application of eCG were effective for producing follicles of 7 mm and COCs acceptable for recovery in Alpacas.
|
This research funded by CIENCIACTIVA-CONCYTEC as part of the project title “Role of seminal plasma in reproductive physiology and application of biotechnologies in camelids” (149-2017).


