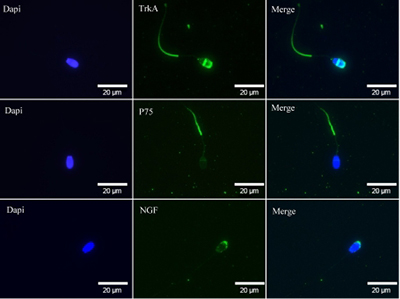
The nerve growth factor β (β-NGF) plays important roles in reproduction in camelid and ruminant females. Less is known about it in males, specifically in rams; however, this study reports the presence of β-NGF in ram spermatozoa for the first time. This finding contributes to a better understanding of the possible roles in animal reproduction. Image by Rodrigo Carrasco.

Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 37 Number 12 2025
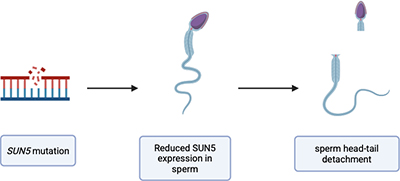
Infertility is a growing concern for many men worldwide, and understanding its genetic causes could lead to better treatments. This study reveals a new mutation in the SUN5 gene, responsible for a condition called acephalic spermatozoa syndrome, where sperm lack heads. These findings offer new insights into male infertility, potentially paving the way for improved diagnosis and personalized therapies for affected individuals. Image created with BioRender.
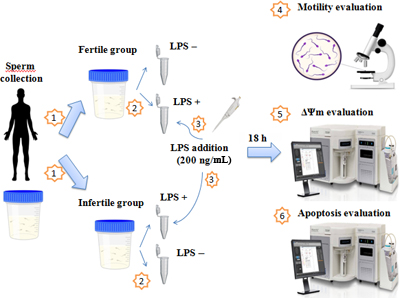
Genital infection represents a potential factor that could induce detrimental effects on male fertility. It has been suggested that lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a major component of Gram-negative bacteria, could have a negative effect on sperm quality. Our study made an attempt to explore the effect of LPS on human sperms and our data strongly suggest that LPS impairs mitochondrial membrane potential and leads to the activation of some pathways responsible for sperm apoptosis, notably in sperms from infertile men. Diagram by Sana Sahnoun.
The growing interest in camels for racing, milk production and beauty competitions has generated enthusiasm to breed from genetically superior animals by using embryo transfer (ET). One of the major challenges of ET is getting large numbers of recipients synchronized with the donor for the day of transfer. However, it is possible to store embryos at 4°C for 2–3 days and addition of catalase to the cooling medium enhances overall pregnancy rates. This therefore reduces the need for such tight synchronization. Image by JA Skidmore.
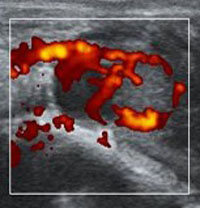
High reproductive performance in beef herds is essential to ensure maximum production and satisfactory economic returns. In this regard, the use of Doppler ultrasound imaging is crucial for enhancing productivity by detecting non-pregnant animals early, allowing for timely resynchronization and reduction in calving intervals. The objective of this study was to evaluate early pregnancy markers for their accuracy and to elucidate the interactions among these reproductive markers. Image by Mariana Alves de Andrande Silva.
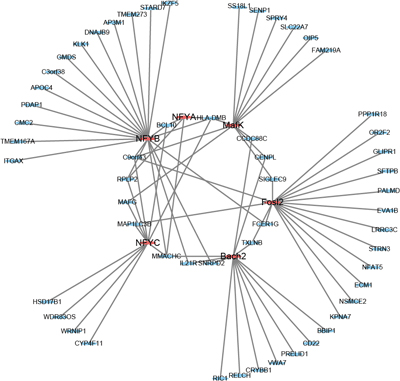
Female infertility impacts millions globally, prompting the exploration of stem cell-derived oocyte technologies as a transformative solution. Cross-species research has identified NFYA/B/C as core regulators of oogenesis, with NFYA demonstrating a remarkable ability to activate the key oocyte-specific gene Alkbh5. This breakthrough promises to elevate the efficiency of in vitro oocyte production while establishing theoretical foundations for novel infertility treatments. Diagram by Shu Fang.