
Environmental Chemistry
Volume 17 Number 4 2020
Antimony in the Environment: A Chinese Perspective
EN19195Association of plasma antimony concentration with markers of liver function in Chinese adults

Environmental context. Antimony pollution has become a global issue given its wide distribution in the environment and its potential threat to human health. This large population-based study demonstrated that exposure to high levels of antimony may impair liver function in adults. The study highlights the potential hazard to liver function of antimony exposure, and provides convincing evidence of the need to monitor and control antimony exposure in the prevention of liver dysfunction.
Environmental context. Phytoremediation requires an understanding of bioconcentration and translocation processes that determine behaviour and fate of potentially toxic elements. We studied the distribution of antimony and arsenic in terrestrial and aquatic soil-plant systems in an antimony ore zone. We found that the common climbing plant Kudzu (Pueraria lobata) is suitable for phyto-stabilisation of antimony-bearing tailings, while tiger grass (Thysanolaena maxima) was able to extract antimony and arsenic from contaminated soils.
Environmental context. Antimony (Sb) contamination from mining is an emergent environmental issue, and there is an urgent need for the development of effective water treatment technology. This study reports a complete Sb remediation strategy using granular titanium dioxide as the adsorbent, and describes adsorbent manufacture, Sb adsorptive removal and regeneration of the adsorbent. The findings highlight a practical way for on-site remediation of Sb-contaminated water.
EN20002Efficient removal of antimony with natural secondary iron minerals: effect of structural properties and sorption mechanism
 , Nairui Deng, Yuyin Qiu, Zebin Su, Chujie Huang, Kaimei Hu, Jianqiao Wang, Liang Ma, Enzong Xiao and Tangfu Xiao
, Nairui Deng, Yuyin Qiu, Zebin Su, Chujie Huang, Kaimei Hu, Jianqiao Wang, Liang Ma, Enzong Xiao and Tangfu Xiao 
Environmental context. Antimony is classified as a priority pollutant and is increasingly detected in the environment as a result of various anthropogenic activities. Natural secondary iron minerals are important sinks for many toxic elements. We found that antimony promotes structural transformations in secondary iron minerals, and that antimony is then further immobilised by the newly formed iron mineral phases.
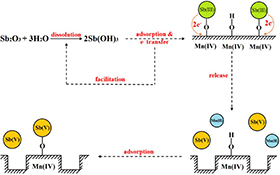
Environmental context. The release of antimony and its compounds to the environment can present a toxic hazard for humans. We evaluated the use of birnessite to dissolve antimony trioxide and found that birnessite accelerated the dissolution process, and ~50 % of the oxidised antimony was absorbed. The results can help evaluate the bioavailability of antimony in the environment.



