Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 32
Number 7 2020
Our health during adulthood begins as early as fertilisation. The Society for Reproductive Biology (SRB) in Australia supports research into the crucial factors governing reproductive health that underlie our ability to improve the health of future generations. This review captures highlights from the SRB annual meeting held in Sydney in August 2019.
Body mass index (BMI) is associated with cardiovascular risk but not necessarily male fertility. So, the aim of this study was to establish, by studying >20 000 patients, one or more BMI reference values that may be used to classify men according to their chance of having semen abnormalities. This recategorisation showed that having a BMI <20 or >32 kg m−2 is associated with a decrease in semen quality and that these negative associations are increased for BMI >37 kg m−2 and are even further increased for BMI >42 kg m−2.
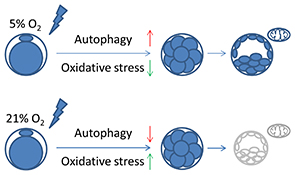
In this study we demonstrate that autophagy may be an effective mechanism to promote embryo development under low oxygen culture conditions. Low oxygen-induced autophagy alleviated oxidative stress, maintained a functional complement of mitochondria and improved embryo development in the pig. These findings help improve our understanding of the function of autophagy, which may be a novel strategy to improve embryo development.
This study investigated the effects of changes in lipid metabolism on porcine IVM oocytes. The study shows that adipolysis is affected by specific lipase and is closely related to mitochondrial function, as indicated by changes in mitochondrial temperature. This reminds us that cytoplasm lipids can be modulated during IVM and that this is related to mitochondrial function.
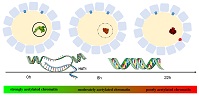
Exploration of methylation characteristics of in vitro-produced (IVP) and in vivo-derived embryos can help improve the quality of IVP embryos. In this study, methylation patterns of IVP and in vivo-derived blastocysts were investigated by single-cell genome methylation sequencing, and the differentially methylated regions identified were primarily involved in oocyte maturation and activation. More attention should be paid to oocyte factors to improve the quality of IVP embryos.
Heterogeneous oocytes with different levels of competence decrease the efficiency of the in vitro production of embryos. Since histone acetylation seems to be related to oocyte competence, the objective of this study was to evaluate the acetylation status of in vitro-matured oocytes of different competences. There was transcription of the HAT1 gene only in competent oocytes during in vitro maturation.
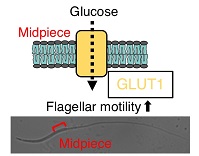
Despite the importance of glucose transport for supporting sperm motility, glucose metabolic pathways are poorly characterised in chicken spermatozoa. We found that the glucose transporter GLUT1 is specifically localised to the midpiece and flagellum, and contributes to flagellar motility by ATP production via glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. These results provide new insights into energy production pathways responsible for avian sperm motility.
This study describes, for the first time, the expression and subcellular localisation of lncRNA5512. To define the role of lncRNA5512 in mouse reproduction, we generated mice homozygous for a null mutation of lncRNA5512; the lncRNA5512-knockout mice showed normal spermatogenesis and fertility. This work has revealed some characteristics of lncRNA5512 and will help further research on long non-coding RNAs.
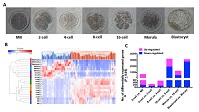
Using the RNA sequencing technologies, we obtained the first complete transcriptome of in vivo goat mature oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Embryonic genome activation occurred at the 16-cell stage, and unique gene regulators of embryo development were identified. Comparison of transcriptomes between mammalian species indicated both conserved and goat-specific features of preimplantation development.