Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 34
Number 8 2022
The prevalence of infertility in the world among couples in reproductive ages is 10–15%. Recent progress in assisted reproductive technology (ART) has made a huge impact on in vitro fertilisation in the last two decades. The increasing success of ART is highly dependent on embryo quality assessment methods. It seems that the use of biomarkers such as specific miRNAs that are released from embryos into the spent culture media can potentially reflect the status of the embryo, and can be useful in ART.
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is frequently used as a solvent in biological studies and as a vehicle for drug therapy and it detrimentally affects porcine embryonic development. This study investigated the mechanism of this process in parthenogenetically activated porcine embryos. DMSO can cause defects in embryonic development by affecting genome-wide DNA methylation and histone modification, and by influencing the expression level of pluripotent genes.
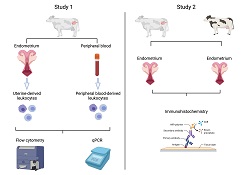
It is still unclear what immunological mechanisms contribute to the successful development of a baby inside the mother’s womb in cattle. We have shown that during pregnancy, immune cells derived from the uterus are present in different numbers and express different genes compared with immune cells derived from blood. Identifying the changes in immune cells during pregnancy is the first step in determining potential measures to increase pregnancy rates in cattle.
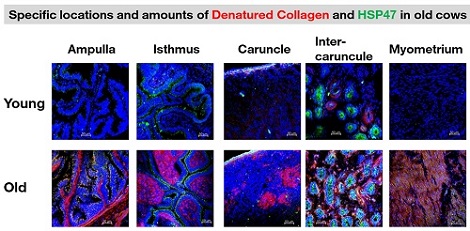
Collagen, a protein that is the most abundant in the oviducts and uteri, is vital for fertility. We developed a new method to compare damaged collagen in the oviducts and uteri of post-pubertal nulliparous heifers and old multiparous cows. Damaged collagen was increased in the oviducts and uteri of old cows. This study also found that the amounts of collagen-specific molecular chaperone HSP47 protein was higher in the oviducts and uteri of the old cows than the heifers.
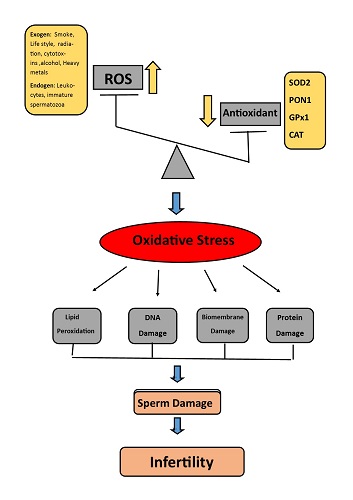
An imbalance between antioxidants and oxidants increases reactive oxygen species, which damages proteins, cell membranes, DNA, peroxidation lipid, and ultimately damages spermatozoa and leads to male infertility. Our findings demonstrate that alleles Arg-PON1 and Ala-MnSOD antioxidant variant genotypes are considerably linked with a higher risk of male infertility. In addition, linear regression analysis revealed that those with the PON1 Gln192Arg or SOD2 Val16Ala variants have significantly higher levels of sperm DNA fragmentation and lower levels of the total antioxidant capacity in seminal fluid.
 and Behrooz Niknafs
and Behrooz Niknafs