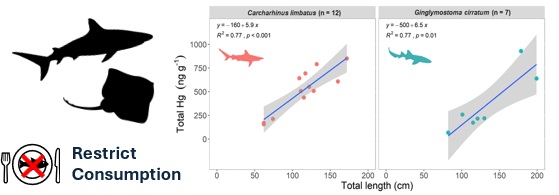
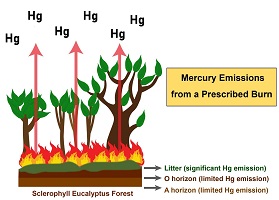
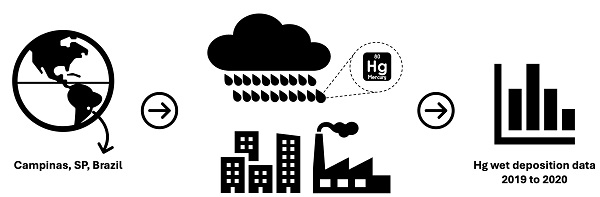
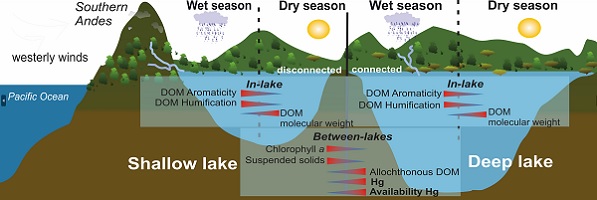
Mercury remains a contaminant of environmental concern, largely as a consequence of historical activities. By its nature, the assessment of the distribution, behaviour and impacts of mercury on aquatic, terrestrial and atmospheric environments requires a multidisciplinary approach, primarily based on environmental chemistry, but supplemented with expertise in ecotoxicology, ecology and archaeology.
In Australia, an active group of researchers came together in 2020, under the umbrella of Mercury Australia [external link] to share information on the historical and contemporary uses and impacts of mercury on the environment and human health. Members are strongly networked to other international researchers, in particular, those in the Southern Hemisphere. Mercury Australia holds bi-annual symposia at which latest research is presented.
This collection contains six papers representing the state-of-the-art in mercury investigations, largely originating from a symposium held in Canberra in July 2023.
Guest Editors:
Graeme Batley, Adjunct Fellow, Macquarie University, Australia
Larissa Schneider, Associate Professor, The Australian National University, Australia
Last Updated: 04 Jul 2025