Hepatitis B virus surface protein induces oxidative stress by increasing peroxides and inhibiting antioxidant defences in human spermatozoa
Lin Cheng A B C * , Pingnan Sun A B C * , Xiaoling Xie A B C , Dongmei Sun D , Qi Zhou A B C , Shaozhe Yang A B C , Qingdong Xie A B C and Xiaoling Zhou A B C E
A B C E
A Stem Cell Research Center, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, PR China.
B Research Center for Reproductive Medicine, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, PR China.
C Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Infectious Diseases and Molecular Immunopathology, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou 515041, PR China.
D Shenzhen Longgang District Maternity & Child Healthcare Hospital, Shenzhen 518172, PR China.
E Corresponding author. Email: xlzhou@stu.edu.cn
Reproduction, Fertility and Development 32(14) 1180-1189 https://doi.org/10.1071/RD20130
Submitted: 16 May 2020 Accepted: 10 August 2020 Published: 1 October 2020
Journal Compilation © CSIRO 2020 Open Access CC BY-NC-ND
Abstract
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection may affect sperm motility in patients with HBV. HBV surface protein (HBs) decreases mitochondrial membrane potential, impairs motility and induces apoptotic-like changes in human spermatozoa. However, little is known about how human spermatozoa respond to reactive oxygen species (ROS; mainly peroxides) induced by HBs. In this study, HBs induced supraphysiological ROS levels in human spermatozoa and reduced the formation of 2-cell embryos (obtained from hamster oocytes and human spermatozoa). HBs induced a pre-apoptotic status in human spermatozoa, as well as antioxidant defences by increasing glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) and peroxiredoxin 5 (PRDX5) levels. These results highlight the molecular mechanism responsible for the oxidative stress in human spermatozoa exposed to HBV and the antioxidant defence response involving GPX4 and PRDX5.
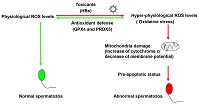
Keywords: 2-cell embryo, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), peroxiredoxin 5 (PRDX5).
References
Aitken, R. J., and Curry, B. J. (2011). Redox regulation of human sperm function: from the physiological control of sperm capacitation to the etiology of infertility and DNA damage in the germ line. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 14, 367–381.| Redox regulation of human sperm function: from the physiological control of sperm capacitation to the etiology of infertility and DNA damage in the germ line.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 20522002PubMed |
Aitken, R. J., Jones, K. T., and Robertson, S. A. (2012). Reactive oxygen species and sperm function – in sickness and in health. J. Androl. 33, 1096–1106.
| Reactive oxygen species and sperm function – in sickness and in health.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 22879525PubMed |
Bourc’his, D., and Voinnet, O. (2010). A small-RNA perspective on gametogenesis, fertilization, and early zygotic development. Science 330, 617–622.
| A small-RNA perspective on gametogenesis, fertilization, and early zygotic development.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 21030645PubMed |
Clarke, D. J. B., Kuleshov, M. V., Schilder, B. M., Torre, D., Duffy, M. E., Keenan, A. B., Lachmann, A., Feldmann, A. S., Gundersen, G. W., Silverstein, M. C., Wang, Z., and Ma’ayan, A. (2018). eXpression2Kinases (X2K) web: linking expression signatures to upstream cell signaling networks. Nucleic Acids Res 46, W171–W179.
| eXpression2Kinases (X2K) web: linking expression signatures to upstream cell signaling networks.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
Dadoune, J. P. (2009). Spermatozoal RNAs: what about their functions? Microsc. Res. Tech. 72, 536–551.
| Spermatozoal RNAs: what about their functions?Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19283828PubMed |
Dai, P., Wang, X., Gou, L. T., Li, Z. T., Wen, Z., Chen, Z. G., Hua, M. M., Zhong, A., Wang, L., Su, H., Wan, H., Qian, K., Liao, L., Li, J., Tian, B., Li, D., Fu, X. D., Shi, H. J., Zhou, Y., and Liu, M. F. (2019). A translation-activating function of MIWI/piRNA during mouse spermiogenesis. Cell 179, 1566–1581.e16.
| A translation-activating function of MIWI/piRNA during mouse spermiogenesis.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 31835033PubMed |
de Lamirande, E., Jiang, H., Zini, A., Kodama, H., and Gagnon, C. (1997). Reactive oxygen species and sperm physiology. Rev. Reprod. 2, 48–54.
| Reactive oxygen species and sperm physiology.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 9414465PubMed |
Elkon, R., Zlotorynski, E., Zeller, K. I., and Agami, R. (2010). Major role for mRNA stability in shaping the kinetics of gene induction. BMC Genomics 11, 259.
| Major role for mRNA stability in shaping the kinetics of gene induction.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 20409322PubMed |
Fan, J., Yang, X., Wang, W., Wood, W. H., Becker, K. G., and Gorospe, M. (2002). Global analysis of stress-regulated mRNA turnover by using cDNA arrays. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 10611–10616.
| Global analysis of stress-regulated mRNA turnover by using cDNA arrays.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 12149460PubMed |
Friedel, C. C., Dolken, L., Ruzsics, Z., Koszinowski, U. H., and Zimmer, R. (2009). Conserved principles of mammalian transcriptional regulation revealed by RNA half-life. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e115.
| Conserved principles of mammalian transcriptional regulation revealed by RNA half-life.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19561200PubMed |
Gur, Y., and Breitbart, H. (2006). Mammalian sperm translate nuclear-encoded proteins by mitochondrial-type ribosomes. Genes Dev. 20, 411–416.
| Mammalian sperm translate nuclear-encoded proteins by mitochondrial-type ribosomes.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16449571PubMed |
Hadchouel, M., Scotto, J., Huret, J. L., Molinie, C., Villa, E., Degos, F., and Brechot, C. (1985). Presence of HBV DNA in spermatozoa: a possible vertical transmission of HBV via the germ line. J. Med. Virol. 16, 61–66.
| Presence of HBV DNA in spermatozoa: a possible vertical transmission of HBV via the germ line.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 3840197PubMed |
Horvathova, I., Voigt, F., Kotrys, A. V., Zhan, Y., Artus-Revel, C. G., Eglinger, J., Stadler, M. B., Giorgetti, L., and Chao, J. A. (2017). The dynamics of mRNA turnover revealed by single-molecule imaging in single cells. Mol. Cell 68, 615–625.e9.
| The dynamics of mRNA turnover revealed by single-molecule imaging in single cells.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 29056324PubMed |
Huang, J. M., Huang, T. H., Qiu, H. Y., Fang, X. W., Zhuang, T. G., and Qiu, J. W. (2002). Studies on the integration of hepatitis B virus DNA sequence in human sperm chromosomes. Asian J. Androl. 4, 209–212.
| 12364978PubMed |
Huang, J. M., Huang, T. H., Qiu, H. Y., Fang, X. W., Zhuang, T. G., Liu, H. X., Wang, Y. H., Deng, L. Z., and Qiu, J. W. (2003). Effects of hepatitis B virus infection on human sperm chromosomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 9, 736–740.
| Effects of hepatitis B virus infection on human sperm chromosomes.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 12679922PubMed |
Huang, J., Zhong, Y., Fang, X., Xie, Q., Kang, X., Wu, R., Li, F., Xu, X., Lu, H., Xu, L., and Huang, T. (2013). Hepatitis B virus s protein enhances sperm apoptosis and reduces sperm fertilizing capacity in vitro. PLoS One 8, e68688.
| Hepatitis B virus s protein enhances sperm apoptosis and reduces sperm fertilizing capacity in vitro.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 24391762PubMed |
Imai, H., Hakkaku, N., Iwamoto, R., Suzuki, J., Suzuki, T., Tajima, Y., Konishi, K., Minami, S., Ichinose, S., Ishizaka, K., Shioda, S., Arata, S., Nishimura, M., Naito, S., and Nakagawa, Y. (2009). Depletion of selenoprotein GPx4 in spermatocytes causes male infertility in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 32522–32532.
| Depletion of selenoprotein GPx4 in spermatocytes causes male infertility in mice.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19783653PubMed |
Kang, X., Xie, Q., Zhou, X., Li, F., Huang, J., Liu, D., and Huang, T. (2012). Effects of hepatitis B virus s protein exposure on sperm membrane integrity and functions. PLoS One 7, e33471.
| Effects of hepatitis B virus s protein exposure on sperm membrane integrity and functions.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23272113PubMed |
Kinowaki, Y., Kurata, M., Ishibashi, S., Ikeda, M., Tatsuzawa, A., Yamamoto, M., Miura, O., Kitagawa, M., and Yamamoto, K. (2018). Glutathione peroxidase 4 overexpression inhibits ROS-induced cell death in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Lab. Invest. 98, 609–619.
| Glutathione peroxidase 4 overexpression inhibits ROS-induced cell death in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 29463878PubMed |
Liang, H., Van Remmen, H., Frohlich, V., Lechleiter, J., Richardson, A., and Ran, Q. (2007). Gpx4 protects mitochondrial ATP generation against oxidative damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 356, 893–898.
| Gpx4 protects mitochondrial ATP generation against oxidative damage.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 17395155PubMed |
Liaw, Y. F., and Chu, C. M. (2009). Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 373, 582–592.
| Hepatitis B virus infection.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19217993PubMed |
Livak, K. J., and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(–Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25, 402–408.
| Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(–Delta Delta C(T)) method.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 11846609PubMed |
Lorusso, F., Palmisano, M., Chironna, M., Vacca, M., Masciandaro, P., Bassi, E., Selvaggi Luigi, L., and Depalo, R. (2010). Impact of chronic viral diseases on semen parameters. Andrologia 42, 121–126.
| Impact of chronic viral diseases on semen parameters.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 20384803PubMed |
Marchetti, C., Obert, G., Deffosez, A., Formstecher, P., and Marchetti, P. (2002). Study of mitochondrial membrane potential, reactive oxygen species, DNA fragmentation and cell viability by flow cytometry in human sperm. Hum Reprod 17, 1257–1265.
| Study of mitochondrial membrane potential, reactive oxygen species, DNA fragmentation and cell viability by flow cytometry in human sperm.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 11980749PubMed |
Moretti, E., Federico, M. G., Giannerini, V., and Collodel, G. (2008a). Sperm ultrastructure and meiotic segregation in a group of patients with chronic hepatitis B and C. Andrologia 40, 173–178.
| Sperm ultrastructure and meiotic segregation in a group of patients with chronic hepatitis B and C.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 18477204PubMed |
Moretti, E., Federico, M. G., Giannerini, V., and Collodel, G. (2008b). Sperm ultrastructure and meiotic segregation in a group of patients with chronic hepatitis B and C. Andrologia 40, 286–291.
| Sperm ultrastructure and meiotic segregation in a group of patients with chronic hepatitis B and C.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 18811918PubMed |
Morielli, T., and O’Flaherty, C. (2015). Oxidative stress impairs function and increases redox protein modifications in human spermatozoa. Reproduction 149, 113–123.
| Oxidative stress impairs function and increases redox protein modifications in human spermatozoa.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25385721PubMed |
O’Flaherty, C. (2014a). The enzymatic antioxidant system of human spermatozoa. Adv. Androl. 2014, 1–15.
| The enzymatic antioxidant system of human spermatozoa.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar |
O’Flaherty, C. (2014b). Peroxiredoxins: hidden players in the antioxidant defence of human spermatozoa. Basic Clin. Androl. 24, 4.
| Peroxiredoxins: hidden players in the antioxidant defence of human spermatozoa.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25780579PubMed |
O’Flaherty, C., and de Souza, A. R. (2011). Hydrogen peroxide modifies human sperm peroxiredoxins in a dose-dependent manner. Biol. Reprod. 84, 238–247.
| Hydrogen peroxide modifies human sperm peroxiredoxins in a dose-dependent manner.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 20864641PubMed |
Oger, P., Yazbeck, C., Gervais, A., Dorphin, B., Gout, C., Jacquesson, L., Ayel, J. P., Kahn, V., and Rougier, N. (2011). Adverse effects of hepatitis B virus on sperm motility and fertilization ability during IVF. Reprod. Biomed. Online 23, 207–212.
| Adverse effects of hepatitis B virus on sperm motility and fertilization ability during IVF.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 21665545PubMed |
Ostermeier, G. C., Dix, D. J., Miller, D., Khatri, P., and Krawetz, S. A. (2002). Spermatozoal RNA profiles of normal fertile men. Lancet 360, 772–777.
| Spermatozoal RNA profiles of normal fertile men.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 12241836PubMed |
Piomboni, P., Focarelli, R., Stendardi, A., Ferramosca, A., and Zara, V. (2012). The role of mitochondria in energy production for human sperm motility. Int. J. Androl. 35, 109–124.
| The role of mitochondria in energy production for human sperm motility.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 21950496PubMed |
Qian, W. P., Tan, Y. Q., Chen, Y., Peng, Y., Li, Z., Lu, G. X., Lin, M. C., Kung, H. F., He, M. L., and Shing, L. K. (2005). Rapid quantification of semen hepatitis B virus DNA by real-time polymerase chain reaction. World J. Gastroenterol. 11, 5385–5389.
| Rapid quantification of semen hepatitis B virus DNA by real-time polymerase chain reaction.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16149152PubMed |
Rabani, M., Levin, J. Z., Fan, L., Adiconis, X., Raychowdhury, R., Garber, M., Gnirke, A., Nusbaum, C., Hacohen, N., Friedman, N., Amit, I., and Regev, A. (2011). Metabolic labeling of RNA uncovers principles of RNA production and degradation dynamics in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 436–442.
| Metabolic labeling of RNA uncovers principles of RNA production and degradation dynamics in mammalian cells.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 21516085PubMed |
Schweitzer, A., Horn, J., Mikolajczyk, R. T., Krause, G., and Ott, J. J. (2015). Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet 386, 1546–1555.
| Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 26231459PubMed |
Scott, R. M., Snitbhan, R., Bancroft, W. H., Alter, H. J., and Tingpalapong, M. (1980). Experimental transmission of hepatitis B virus by semen and saliva. J. Infect. Dis. 142, 67–71.
| Experimental transmission of hepatitis B virus by semen and saliva.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 7400629PubMed |
Sendler, E., Johnson, G. D., Mao, S., Goodrich, R. J., Diamond, M. P., Hauser, R., and Krawetz, S. A. (2013). Stability, delivery and functions of human sperm RNAs at fertilization. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 4104–4117.
| Stability, delivery and functions of human sperm RNAs at fertilization.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23471003PubMed |
Shi, L., Liu, S., Zhao, W., Zhou, H., Ren, W., and Shi, J. (2014). Hepatitis B virus infection reduces fertilization ability during in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. J. Med. Virol. 86, 1099–1104.
| Hepatitis B virus infection reduces fertilization ability during in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 24760595PubMed |
Su, F. H., Chang, S. N., Sung, F. C., Su, C. T., Shieh, Y. H., Lin, C. C., and Yeh, C. C. (2014). Hepatitis B virus infection and the risk of male infertility: a population-based analysis. Fertil. Steril. 102, 1677–1684.
| Hepatitis B virus infection and the risk of male infertility: a population-based analysis.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25439807PubMed |
Vicari, E., Arcoria, D., Di Mauro, C., Noto, R., Noto, Z., and La Vignera, S. (2006). Sperm output in patients with primary infertility and hepatitis B or C virus; negative influence of HBV infection during concomitant varicocele. Minerva Med. 97, 65–77.
| 16565700PubMed |
Vourekas, A., Alexiou, P., Vrettos, N., Maragkakis, M., and Mourelatos, Z. (2016). Sequence-dependent but not sequence-specific piRNA adhesion traps mRNAs to the germ plasm. Nature 531, 390–394.
| Sequence-dependent but not sequence-specific piRNA adhesion traps mRNAs to the germ plasm.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 26950602PubMed |
Wang, G., Guo, Y., Zhou, T., Shi, X., Yu, J., Yang, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, J., Liu, M., Chen, X., Tu, W., Zeng, Y., Jiang, M., Li, S., Zhang, P., Zhou, Q., Zheng, B., Yu, C., Zhou, Z., Guo, X., and Sha, J. (2013). In-depth proteomic analysis of the human sperm reveals complex protein compositions. J. Proteomics 79, 114–122.
| In-depth proteomic analysis of the human sperm reveals complex protein compositions.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 23268119PubMed |
Watanabe, T., Cheng, E. C., Zhong, M., and Lin, H. (2015). Retrotransposons and pseudogenes regulate mRNAs and lncRNAs via the piRNA pathway in the germline. Genome Res. 25, 368–380.
| Retrotransposons and pseudogenes regulate mRNAs and lncRNAs via the piRNA pathway in the germline.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 25480952PubMed |
Yoshida, K., Muratani, M., Araki, H., Miura, F., Suzuki, T., Dohmae, N., Katou, Y., Shirahige, K., Ito, T., and Ishii, S. (2018). Mapping of histone-binding sites in histone replacement-completed spermatozoa. Nat. Commun. 9, 3885.
| Mapping of histone-binding sites in histone replacement-completed spermatozoa.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 30250204PubMed |
Zhao, Y., Li, Q., Yao, C., Wang, Z., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, L., Wang, L., and Qiao, Z. (2006). Characterization and quantification of mRNA transcripts in ejaculated spermatozoa of fertile men by serial analysis of gene expression. Hum. Reprod. 21, 1583–1590.
| Characterization and quantification of mRNA transcripts in ejaculated spermatozoa of fertile men by serial analysis of gene expression.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 16501037PubMed |
Zhao, C., Guo, X. J., Shi, Z. H., Wang, F. Q., Huang, X. Y., Huo, R., Zhu, H., Wang, X. R., Liu, J. Y., Zhou, Z. M., and Sha, J. H. (2009). Role of translation by mitochondrial-type ribosomes during sperm capacitation: an analysis based on a proteomic approach. Proteomics 9, 1385–1399.
| Role of translation by mitochondrial-type ribosomes during sperm capacitation: an analysis based on a proteomic approach.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19253287PubMed |
Zhong, C., Lu, H., Han, T., Tan, X., Li, P., Huang, J., Xie, Q., Hou, Z., Qu, T., Jiang, Y., Wang, S., Xu, L., Zhong, Y., and Huang, T. (2017). CpG methylation participates in regulation of hepatitis B virus gene expression in host sperm and sperm-derived embryos. Epigenomics 9, 123–125.
| CpG methylation participates in regulation of hepatitis B virus gene expression in host sperm and sperm-derived embryos.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 27919171PubMed |
Zhong, Y., Liu, D. L., Ahmed, M. M. M., Li, P. H., Zhou, X. L., Xie, Q. D., Xu, X. Q., Han, T. T., Hou, Z. W., Huang, J. H., Xu, L., and Huang, T. H. (2018). Transcription and regulation of hepatitis B virus genes in host sperm cells. Asian J. Androl. 20, 284–289.
| Transcription and regulation of hepatitis B virus genes in host sperm cells.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 29111540PubMed |
Zhou, X. L., Sun, P. N., Huang, T. H., Xie, Q. D., Kang, X. J., and Liu, L. M. (2009). Effects of hepatitis B virus S protein on human sperm function. Hum. Reprod. 24, 1575–1583.
| Effects of hepatitis B virus S protein on human sperm function.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 19279032PubMed |
Zini, A., de Lamirande, E., and Gagnon, C. (1993). Reactive oxygen species in semen of infertile patients: levels of superoxide dismutase- and catalase-like activities in seminal plasma and spermatozoa. Int J Androl 16, 183–188.
| Reactive oxygen species in semen of infertile patients: levels of superoxide dismutase- and catalase-like activities in seminal plasma and spermatozoa.Crossref | GoogleScholarGoogle Scholar | 8359932PubMed |
Zini, A., De Lamirande, E., and Gagnon, C. (1995). Low levels of nitric oxide promote human sperm capacitation in vitro. J. Androl. 16, 424–431.
| 8575982PubMed |


