Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 75
Number 5 2022
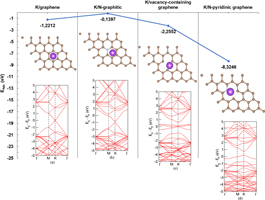
The band structure of graphene, N-graphitic graphene, defect-graphene, and N-pyridinic graphene reveals the band opening features that influence adsorption interactions with K+ ions. The ease with which K+ ions interact on the graphene surface is facilitated by a larger bandgap energy. The bandgap energies of vacantcy-containing graphene and N-pyridine-doped graphene are larger, leading to greater K+ ion interactions. In the pyridine arrangement, the presence of N doping degrades graphene symmetry, changes Fermi levels and increases the bandgap. The greater the bandgap, the stronger the interaction of graphene with K+ ions. The interaction between K+ ions and N-pyridine-doped graphene, however, results in an energy that is too high in this approach.
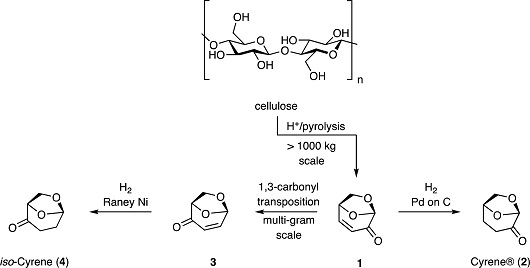
Cyrene® (2), a commercially available solvent, is obtained by hydrogenation of levoglucosenone (LGO, 1), itself the product of pyrolysis of acid-treated cellulose. iso-Cyrene (4) has now been prepared from iso-LGO (3) and shown to display certain complementary solvent properties.
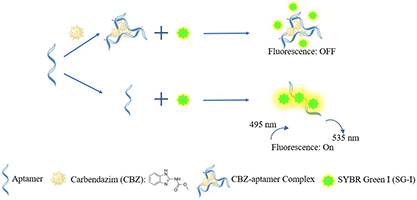
This paper proposes a fluorescent aptasensor for detecting carbendazim (CBZ) based on the interaction among CBZ, CBZ-aptamer and Synergy Brands, SYBR Green I (SG-I). The results show the aptasensor has a linear range from 3.58 to 230 nM and a good limit of detection (LOD) of 3.58 nM.
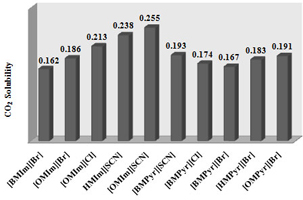
The solubility of CO2 in some of ionic liquids (ILs) was measured. CO2 solubility in ILs with different alkyl chain lengths in the cation increased with increasing alkyl chain length. Also, CO2 solubility increased with increasing anion basicity.
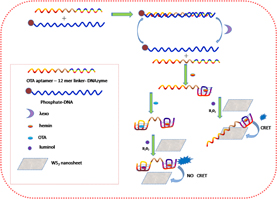
We developed a new amplified chemiluminescence sensing platform based on WS2 nanosheet chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer (CRET) for light on detection of ochratoxin A (OTA). In this study, lambda exonuclease (λexo) was added to catalyse the degradation of phosphate-DNA in the dsDNA, which can then provide a stable supply of a form of the OTA aptamer-12-mer linker-DNAzyme that can easily bind to hemin and OTA.
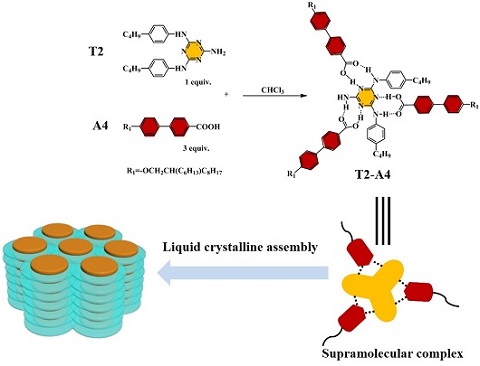
Hydrogen-bonded supramolecules Tx-Ay were prepared by solution blending of triazine derivatives (Tx) and aromatic acids (Ay). 1H NMR and FT-IR results showed that hydrogen-bonded supramolecules were formed in all triazine-aromatic acid groups except T3-A1. DSC and POM analysis indicated that T1-A4, T2-A4 and T4-A4 in A4 series showed columnar liquid crystal behavior in a certain temperature range, while T3-A4 was nematic liquid crystal; WAXS confirmed that T1-A1, T2-A1 and T1-A4 were room temperature columnar liquid crystals.
 , Fitria Rahmawati, Khoirina Dwi Nugrahaningtyas, Abdurro’Uf Althof Abiyyi, Mohamad Zola Erlangga and Nourma Pujiastuti
, Fitria Rahmawati, Khoirina Dwi Nugrahaningtyas, Abdurro’Uf Althof Abiyyi, Mohamad Zola Erlangga and Nourma Pujiastuti