Reproduction, Fertility and Development
Volume 32
Numbers 15 & 16 2020
Maternal high-protein diets or urea treatments have been shown to change gene expression and affect embryo development in bovine and human embryos. However, the effects of high blood urea nitrogen (BUN) on equine embryos are unknown. Oral urea administration to mares resulted in Day 14 embryos with higher urea nitrogen concentrations in the blastocoele fluid and transcriptome changes related to neurological development and urea transport. These findings improve our knowledge regarding the effects of high BUN on equine embryo development.
This is the first report of a coculture system using porcine luteal cells during porcine IVM. The coculture system modified the apoptosis pattern and decreased reactive oxygen species levels in cumulus cells, increased monospermic penetration and IVF efficiency after IVF and increased blastocysts rates after in vitro culture. This model could be an alternative to the conventional maturation medium, giving rise to lower polyspermy and higher blastocysts rates, key issues in in vitro embryo production in pigs.
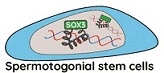
Tightly controlled gene expression is critical for the initiation of spermatogenesis. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, we characterised the genome-wide binding profile of the transcription factor SRY-box transcription factor 3 (SOX3) in mouse Postnatal Day 7 testes, identifying key targets such as neurogenin3 and canonical and testes-specific histones. These data provide valuable insights into some of the fundamental transcriptional mechanisms that drive spermatogonial progenitor cell differentiation.
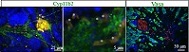
Stem Leydig cells are critical for the formation and maintenance of a functional androgen-producing cell (Leydig cell) population throughout adult male life. A clonal stem Leydig cell line capable of androgen production from 3-month-old Nile tilapia testis has been successfully established. This cell line may offer new opportunities for investigating the self-renewal of stem Leydig cells and steroidogenesis in vitro, and also provide an invaluable in vitro model for screening and investigating endocrine disruptors.
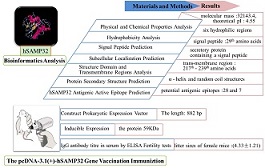
To control rapid population growth, a safe, effective, convenient and reversible contraception method based on sperm antigens needs to be developed. As a testis-specific antigen, human sperm acrosome membrane-associated protein 1 (hSAMP32) contains several transmembrane regions and five antigenic epitopes. We found that the pcDNA-3.1(+)-hSAMP32 immunocontraception vaccine has antifertility effects in BALB/c mice, and may be a potential candidate for an immunocontraceptive vaccine. hSAMP32may warrant further investigation as a new target antigen for immunocontraceptive control.
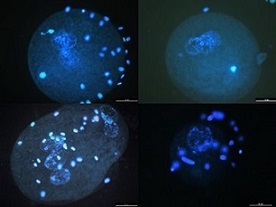
The Egyptian spiny mouse is the world’s only known menstruating rodent. Sperm cryopreservation is a commonly used assisted reproductive technique for preserving the genetics of endangered and laboratory species, but, until now, has not been reported in the spiny mouse. The methods developed and successfully tested here will provide a foundation for future reproductive research and a reliable archive of spiny mouse genetics.
Failure to adequately control for multiple testing is a common problem for many studies published in the reproduction literature. Large genome-wide association studies (GWAS) reliably detect the genetic factors with small effects that contribute to risk for many common diseases. Looking back, almost no genetic risk factors reported from earlier candidate gene studies replicate in these GWAS. These observations demonstrate the importance of study power and adequately accounting for multiple testing to prevent continued publication of false positive association results.
 , Hossam El-Sheikh Ali
, Hossam El-Sheikh Ali  , Pouya Dini
, Pouya Dini  , Shavahn Loux
, Shavahn Loux  , Claudia Barbosa Fernandes
, Claudia Barbosa Fernandes  , Kirsten Scoggin
, Kirsten Scoggin  , Alejandro Esteller-Vico
, Alejandro Esteller-Vico  , Laurie Lawrence and Barry Ball
, Laurie Lawrence and Barry Ball