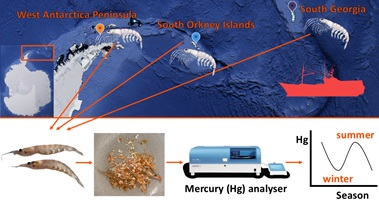
Environmental context. Several predators that eat Antarctic krill may be unintentionally ingesting toxic substances. Studying aspects of krill life to understand the effects of potential increases in Antarctic mercury (Hg) availability revealed that seasons, locations and individual size influence krill Hg concentration. Despite increasing human presence (potential Hg sources) in Antarctica, krill Hg content remains stable, and evidence suggests that Hg accumulates in predators by both short (krill-based) and longer food chains. (Image credit: the authors.)
This article belongs to the collection: Mercury in the environment.
EN24103 Abstract | EN24103 Full Text | EN24103PDF (2.8 MB) | EN24103Supplementary Material (1 MB) Open Access Article