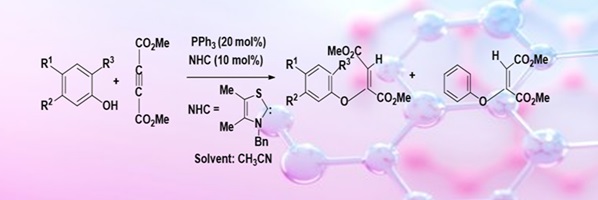
The catalytic activities of triphenylphosphine and N-heterocyclic carbene, namely 3-benzyl-4,5-dimethylthiazolylidene, have been compared by carrying out oxa–Michael additions of some phenols with dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate in the presence of one of these catalysts. The experimental results have been rationalised on the basis of theoretical calculations. (Image credit: Priyanka Suthar.)

Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 78 Number 7 2025
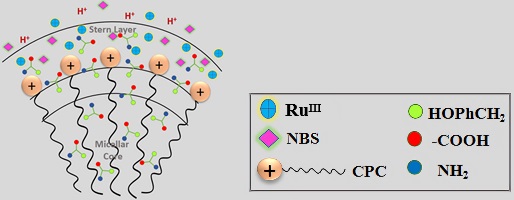
In the CPC micellar environment, the more hydrophobic reactant component (L-Tyrosine) and the extended aliphatic chain of CPC reside in the micelle’s core. The micelle Stern layer preserves the polar components of the surfactant (Me3N+), substrate (–NH2, and –COOH) and reactive species of NBS and RuIII in proximity, hence promoting the oxidation of L-Tyr. The elevated concentration of reactant molecules at the micellar interface enhances the effective collision frequency among the reacting molecules, significantly promoting the oxidation process. (Image credit: Abhishek Srivastava.)
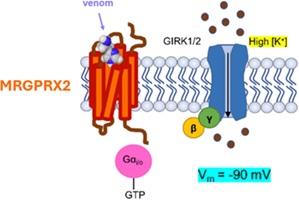
Mast cells of our immune system are generally difficult and expensive to maintain in vitro and, therefore, not economical to use in drug discovery. The development of a bioassay expressing the human mas-related G protein-coupled receptor-X2 receptor linked to potassium channels in a host cell offers a good alternative. (Image credit: Jan Tytgat.)
This article belongs to the collection: 70th Birthday tribute to Professor David Craik.
CH25059 Abstract | CH25059 Full Text | CH25059PDF (1.2 MB) Open Access Article