
Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 72 Numbers 1 & 2 2019
Professor Ken Seddon In Memoriam
CHv72n2_FOKenneth R. Seddon – A Rock Star of Ionic Liquids
The foreword to this special issue of the Journal dedicated to Professor Kenneth R. Seddon provides an account of his distinguished career and his pioneering work in the field of ionic liquids.
CH18541Ionic Liquids – Further Progress on the Fundamental Issues
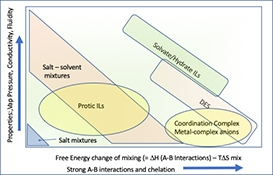
Progress and challenges in addressing the fundamental issues in ionic liquid chemistry are discussed, including the broadening scope of mixture systems that form part of this field, thermal stability, biodegradation, nomenclature, ion pairing, and electrochemical properties.
CH18422Crystal Polymorphism of 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Hexafluorophosphate: Phase Diagram, Structure, and Dynamics
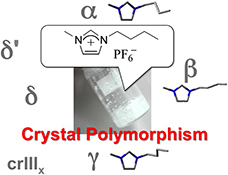
[C4mim]PF6 shows a complex phase behaviour and several phases have been reported so far. Among them, the structure and dynamics for α, β, and γ have been well investigated and the phase behaviour is strongly associated with the cation conformational change.
CH18116Thermal Conductivity Enhancement Phenomena in Ionic Liquid-Based Nanofluids (Ionanofluids)

(Io)nanofluids are very interesting materials for heat transfer processes. They combine the specific properties of ionic liquids (i.e. low vapour pressure), and enhanced thermophysical properties (in particular thermal conductivity) caused by the dispersed nanoparticles. The mechanism and modelling of thermal conductivity are a particular consideration in this work.
CH18104Surface-Active Ionic Liquids in Catalytic Water Splitting
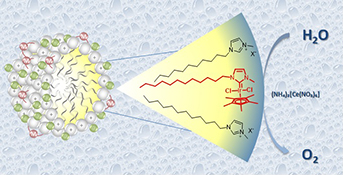
We present the application of imidazolium-based surface-active ionic liquids as ligands and optional reaction media in iridium-catalyzed water oxidations and report a strong influence of ionic liquid concentration in water on the catalytic performance.
CH18187Photo-Luminescence Dynamics of Ionic Liquids Composed of the Dicyanoaurate(I) Anion
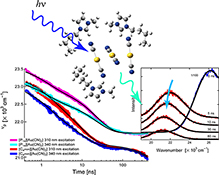
Photo-excitation dynamics of ionic liquids composed of dicyanoaurate(i) have been studied by ultrafast time-resolved luminescence spectroscopy. The low energy band of the dual luminescence bands showed a dynamic shift with time depending on the cation species and excitation wavelength. The shift is discussed in relation to the oligomer formation of anions in the ionic liquids.
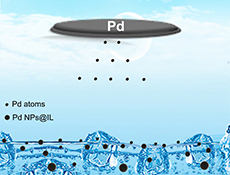
Palladium nanoparticles were prepared in functionalized ionic liquids by magnetic sputtering. The shape and size of the nanoparticles are related to the structure/organisation of ionic liquids used.
CH18170Effect of Alkyl Chain Length in Anions on the Physicochemical Properties of Cellulose-Dissolving Protic Ionic Liquids

A protic ionic liquid (PIL) composed of 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]-undec-7-ene (DBU) and acetic acid can dissolve cellulose under mild conditions and catalyse its transesterification. In this study, PILs composed of DBU and carboxylic acids with varying alkyl chain lengths were prepared, and the relationship between physicochemical properties and chemical structures was investigated.
CH18170 Abstract | CH18170 Full Text | CH18170PDF (417 KB) | CH18170Supplementary Material (312 KB) Open Access Article
CH18253Design of Acyl Donor for Environmentally Benign Acylation of Cellulose Using an Ionic Liquid
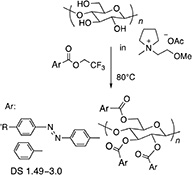
The homogeneous strong base catalyst-free acylation of cellulose using 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl ester as the acyl donor in an ionic liquid, [P1ME][OAc] as the solvent has been accomplished.
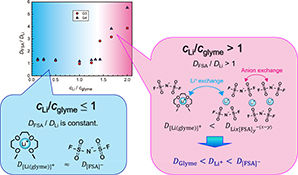
In solvate ionic liquids composed of lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide (Li[FSA]) and glyme, charge transport through the ligand exchange of Li+ emerges when the molar ratio of Li[FSA]/glyme is higher than 1.
CH18270 Abstract | CH18270 Full Text | CH18270PDF (1.2 MB) | CH18270Supplementary Material (337 KB) Open Access Article
CH18361Dissolution of Amyloid Aggregates in Aqueous Ionic Liquid Solutions: A Case Study of Insulin Amyloid
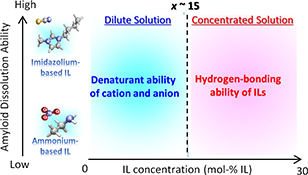
Imidazolium-based ILs showed a higher dissolution ability for bovine insulin amyloid aggregates than ammonium-based ILs for all concentrations of x (x = 0–30 mol-% IL). The mechanisms of dissolution by ILs across a broad IL concentration range for insulin amyloid aggregates is described.
CH18368Crystal Polymorphs and Multiple Crystallization Pathways of Highly Pressurized 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Nitrate
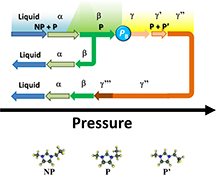
Multiple crystallization pathways of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium nitrate, [C2mim][NO3], were switched at the bifurcation pressure (PB). PB was determined by the high pressure-inherent conformer (P′) of C2mim+ anion.
CH18380Fluctuations and Mixing State of an Aqueous Solution of the Ionic Liquid Tetrabutylphosphonium Trifluoroacetate around the Critical Point
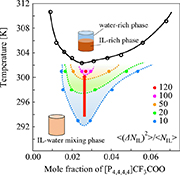
The structural fluctuation and mixing state of aqueous solutions of tetrabutylphosphonium trifluoroacetate, ([P4,4,4,4]CF3COO), which exhibits a lower-critical-solution-temperature-type phase transition, were investigated. The relationship between the mesoscopic fluctuations and the macroscopic phase transition was clarified by drawing a contour map of the fluctuations on the phase diagram.
CH18378Binary Ionic Liquid System for Direct Cellulose Etherification

Several mixtures of ionic liquids, playing roles in both cellulose dissolution and catalysis, were synthesised. Cellulose etherification was performed in these IL mixtures. The proportion of propoxy cellulose exceeded 2.5 after 24 h.
CH18375Microheterogeneity in Ionic Liquid Mixtures: Hydrogen Bonding, Dispersed Ions, and Dispersed Ion Clusters
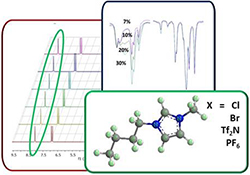
The structural features of IL binary mixtures have been investigated through 1H NMR, FT-IR, thermogravimetric, and solvatochromic measurements.
CH18395Hydrogels Containing the Ferri/Ferrocyanide Redox Couple and Ionic Liquids for Thermocells
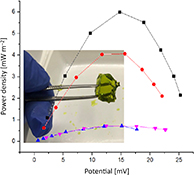
A range of hydrogels incorporating ionic liquids and a redox couple are investigated for use in thermoelectrochemical cells.
CH18396Electrochemical Detection of Explosive Compounds in an Ionic Liquid in Mixed Environments: Influence of Oxygen, Moisture, and Other Nitroaromatics on the Sensing Response
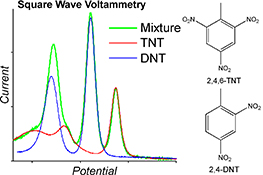
The electroreduction of TNT and DNT in the presence of oxygen, moisture (humidity), and other nitroaromatic compounds is studied. Although currents for TNT were unaffected by oxygen, DNT currents were significantly affected. Humid environments were found to have a large effect on the voltammetry for both compounds. Importantly, DNT and TNT could be separately identified and quantified in a mixture.
CH18384Protic Ionic Liquids Based on Oligomeric Anions [(HSO4)(H2SO4)x]− (x = 0, 1, or 2) for a Clean ϵ-Caprolactam Synthesis
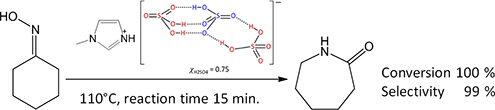
Inexpensive Brønsted-acidic ionic liquids based on nitrogen bases and sulfuric acid, suitable for industrial-scale catalysis, as reaction media and catalysts for the Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime to ϵ-caprolactam are reported. The advantages of the proposed method are a high conversion of oxime with very good selectivity after 15 min of reaction and omission of the neutralisation step.
CH18533A Polar Liquid Zwitterion Does Not Critically Destroy Cytochrome c at High Concentration: An Initial Comparative Study with a Polar Ionic Liquid
A polar liquid zwitterion with a small volume of water dissolves cytochrome c stably, compared with an analogous ionic liquid.
CH18481Using Thermodynamics to Assess the Molecular Interactions of Tetrabutylphosphonium Carboxylate–Water Mixtures
 , Johan Jacquemin, Natalia V. Plechkova, Margarida Costa Gomes and Kenneth R. Seddon
, Johan Jacquemin, Natalia V. Plechkova, Margarida Costa Gomes and Kenneth R. Seddon
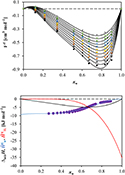
In this study, the interactions between tetrabutylphosphonium carboxylates and water were assessed by thermodynamic measurements. Densities, ρ, viscosities, η, and enthalpies of mixing, ΔmixH, of binary [P4 4 4 4][CnCOO]–water mixtures (with n = 1, 2 or 7) were determined at atmospheric pressure as a function of temperature.
CH18349Cluster–Micelle Transition of a Thermo- and Photoresponsive ABC Triblock Copolymer in an Ionic Liquid
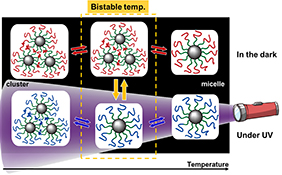
We report the photocontrollable micelle–cluster transition of an ABC triblock copolymer in an ionic liquid. With decreasing temperature, the triblock copolymer changes its self-assembled structure from micelles into clusters due to the aggregation of photo- and thermoresponsive blocks. Under UV irradiation, the micelles form clusters at lower temperatures than that in the dark.



