Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 78
Number 10 2025
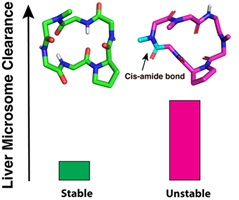
Hepatic stability is crucial for achieving oral bioavailability, as drugs rapidly metabolised by the liver fail to reach effective blood concentrations. This study evaluated the rat liver microsomal stability of N-methylated cyclic hexapeptides. Despite similar sequences, large differences in stability emerged. Poor stability correlated strongly with the presence of cis-amide bonds. NMR and modelling confirmed that cis geometry exposes N-methyl groups to enzymatic attack. These findings identify a cis-amide bond as a key metabolic liability in cyclic peptide drug design. (Image credit: Huy Hoang and Timothy Hill.)
This article belongs to the collection: 70th Birthday tribute to Professor David Craik.
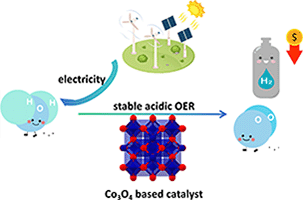
Recent advances in the development of Co3O4-based catalysts for acidic oxygen evolution reaction (OER) are reviewed, highlighting structural, electronic and design strategies to enhance activity and stability for practical proton exchange membrane (PEM) water electrolysis applications. Co3O4 is a promising non-precious alternative to noble metals like IrO2 and RuO2, but long-term stability remains a challenge. The review emphasises key engineering techniques, such as doping, surface modification and defect engineering, to enhance performance for large-scale PEM application. (Image credit: Huihui Li.)
This article belongs to the collection: 2024–25 RACI and AAS Award papers.
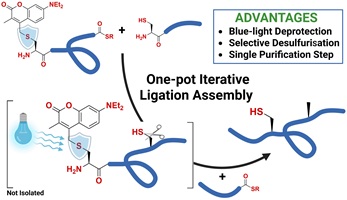
This communication reports an iterative one-pot native chemical ligation–desulfurisation method using 7-diethylamino-3-methyl coumarin (DEAMC) as a cysteine protecting group. Selective desulfurisation is conducted in the presence of DEAMC-protected cysteine, enabling subsequent photodeprotection and ligation without purification. The utility of this strategy was demonstrated by the efficient one-pot synthesis of a 60-residue mucin-1 peptide. (Image credit: Lucas Kambanis.)
This article belongs to the collection: 70th Birthday tribute to Professor David Craik.