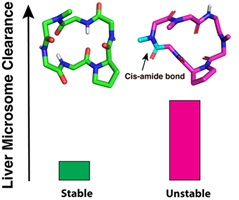
Hepatic stability is crucial for achieving oral bioavailability, as drugs rapidly metabolised by the liver fail to reach effective blood concentrations. This study evaluated the rat liver microsomal stability of N-methylated cyclic hexapeptides. Despite similar sequences, large differences in stability emerged. Poor stability correlated strongly with the presence of cis-amide bonds. NMR and modelling confirmed that cis geometry exposes N-methyl groups to enzymatic attack. These findings identify a cis-amide bond as a key metabolic liability in cyclic peptide drug design. (Image credit: Huy Hoang and Timothy Hill.)
This article belongs to the collection: 70th Birthday tribute to Professor David Craik.
CH25080 Abstract | CH25080 Full Text | CH25080PDF (1.9 MB) | CH25080Supplementary Material (110 KB) Open Access Article