
Australian Journal of Chemistry
Volume 73 Number 8 2020
PhysChem 2019
CHv73n8_FOPhysChem 2019: RACI Australian Conference on Physical Chemistry, Perth, 11–14 February 2019
The foreword to this special issue of the Journal provides an overview of the papers that have been contributed by participants at the 2019 RACI Australian Conference on Physical Chemistry, which was held at the University of Western Australia from 11 to 14 February 2019.
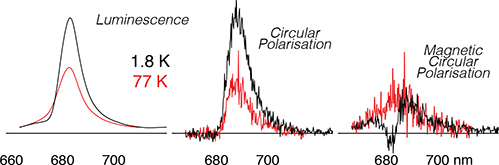
Studies of isolated reaction centre preparations of PS II have been pivotal in the development of models of both the coupling between its pigments and the process of charge separation. Several key puzzles remain in our understanding of these important systems. We apply new and powerful optical techniques (CPL and MCPL) and, by means of an exciton analysis, point to key new ideas.
Experiment and theory work in synergy to develop improved methods for predicting octanol-water partition coefficients (log P).
CH19648 Abstract | CH19648 Full Text | CH19648PDF (794 KB) | CH19648Supplementary Material (282 KB) Open Access Article
CH19571‘Live and Large’: Super-Resolution Optical Fluctuation Imaging (SOFI) and Expansion Microscopy (ExM) of Microtubule Remodelling by Rabies Virus P Protein

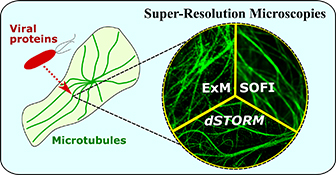
Super-resolution microscopy continues to develop: super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI) is well suited for application in live cells and expansion microscopy (ExM) allows for imaging sub-diffraction detail with conventional microscopes. Here, they are utilised along with single molecule localisation microscopy (dSTORM) to visualise microtubule remodelling by rabies virus P proteins.
CH19428Evidence For a Water-Stabilised Ion Radical Complex: Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Ab Initio Calculations
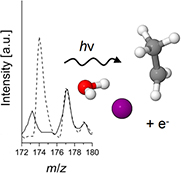
The formation of complexes between water molecules and radicals are important in dictating the processes of a number of atmospheric reactions. Here, a combination of mass spectrometry, phototelectron spectroscopy, and ab initio calculations are used to assign the form of an experimental I−…H2O…CH3CH2 gas-phase radical ion complex.
CH19555Electron Transfer in a Naphthalene Diimide System Studied by Single-Molecule Delayed Fluorescence
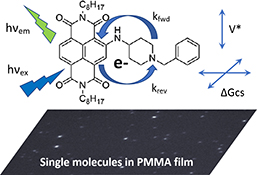
Delayed fluorescence allows detection of single molecules of a naphthalene diimide–tertiary amine system with efficient electron transfer operative. Calculation of forward and reverse rate constants for individual molecules reveals contributions from both coupling and driving force to the distribution of behaviour from molecule to molecule when embedded in a polymer film.
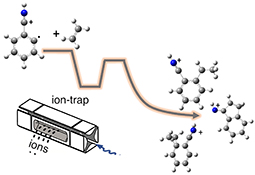
A combination of ion-trap mass spectrometry and gas-phase reactions are used to study radical ions derived from protonated cyanobenzene reacting with ethylene (the archetypal olefin). Molecular weight growth is observed, from barrierless entrance channels – thus, these are viable reactions in the cold environment of space.
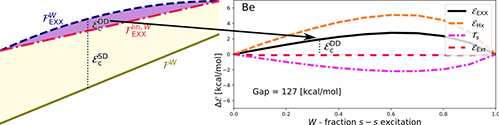
This work develops the theory of density-driven correlations in ensemble density functional theory, to help produce accurate low-cost theories of low-lying excitations.
CH19388Using Molecular Modelling to Understand and Predict the Impact of Organic Additives as Crystal Growth Modifiers
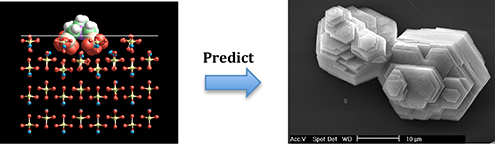
Molecular modelling, through the calculation of replacement energies, provides insights on how organic species will impact the growth rates and resultant morphology of crystals.
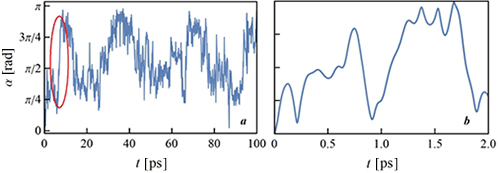
Rotational dynamics of molecules is surprisingly complicated even in apparently simple liquids. We present an analysis of the rotational dynamics of hydrogen sulfide and compare it with that of water. The two liquids have similar molecular geometries but different hydrogen bonding properties. Neither liquid follows the standard Debye model that is traditionally used in the NMR literature to describe molecular reorientation.
CH19448Diatomic Rovibronic Transitions as Potential Probes for Proton-to-Electron Mass Ratio Across Cosmological Time
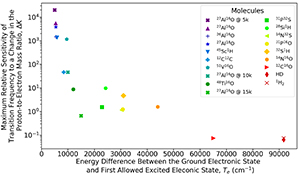
To improve constraints on the variation of the proton-to-electron mass ratio and provide better guidance to theories of new physics, new molecular probes will be useful. From our investigation, we consider criteria to screen potential astrophysical molecules as probes. For rovibronic transitions in diatomic molecules, we find that low-lying electronic states allow for enhanced transitions.
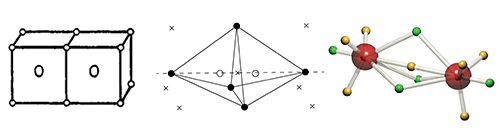
We review the pre-quantum theories of electronic structure of Lewis and Langmuir, and how this relates to the post-quantum double-quartet theory of Linnett. Linnett’s ideas are put on a firm theoretical footing through the emergence of the wavefunction tile: the 3N-dimensional repeating structure of the N-electron wavefunction.
CH19517 Abstract | CH19517 Full Text | CH19517PDF (2.8 MB) Open Access Article
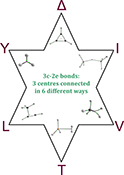
Atoms in molecules (AIM) and natural bond orbital (NBO) analyses have been used to investigate three-centre two-electron bonds and classify them based on their arrangements into either V, L, Δ, Y, T, or I types. These differences in their arrangements lead to differences in their properties.
CH19469The Case for Methyl Group Precession Accompanying Torsional Motion
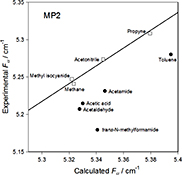
The physical behaviour of the methyl group during internal rotation (torsion) is explored. Precession of the methyl group is shown to give rise to a number of the constants required to fit experimental rotational line data. Quantum chemistry calculations of the optimised molecular structures at key torsional angles provide further evidence that methyl precession occurs.
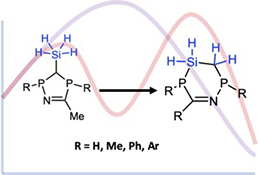
Theoretical investigation of phosphorus heterocyclic carbenes (PHCs): do they behave like NHCs, which undergo ring-insertion by element hydrides (SiH2Ph2, BH2NMe2)?
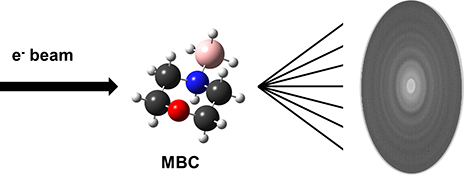
The molecular structure of morpholine borane complex, a candidate for chemical hydrogen storage, has been studied in the solid state and gas phase using single-crystal X-ray diffraction and gas electron diffraction, and its thermochemistry studied computationally. Evolution of hydrogen from the complex is calculated to be close to thermoneutral and spontaneous, thus introducing a new amine borane complex with potential for future on-board hydrogen generation.
CH19502Analysis of Nanoconfined Protein Dielectric Signals Using Charged Amino Acid Network Models
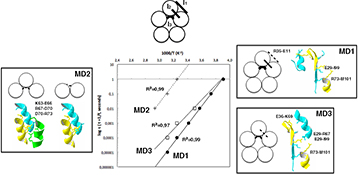
The unfolding of the cholera toxin B pentamer is measured by broadband dielectric spectroscopy in nanoconfined conditions after a 3 h treatment at 80°C, exhibiting three conformations with distinct molecular dynamics. Electrostatic network-based models allow the attribution of thermally disturbed toxin interfaces that underlie the distinct dynamics of the three conformations.
CH19502 Abstract | CH19502 Full Text | CH19502PDF (1.9 MB) | CH19502Supplementary Material (526 KB) Open Access Article
CH19453Probing Intramolecular Interaction of Stereoisomers Using Computational Spectroscopy
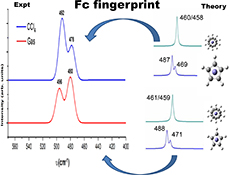
Molecular spectroscopy is a branch of quantum mechanics. Spectroscopic analysis depends on structural information at the molecule level. The earlier experimental measurements of IR spectra of ferrocene (Fc) could neither identify the fingerprints of the Fc conformer nor explain why the gas phase and solution IR spectra have different stereoisomer fingerprints without theoretical support. This article indicates that contemporary molecular spectroscopy needs guidance as well as support from computational spectroscopy.



